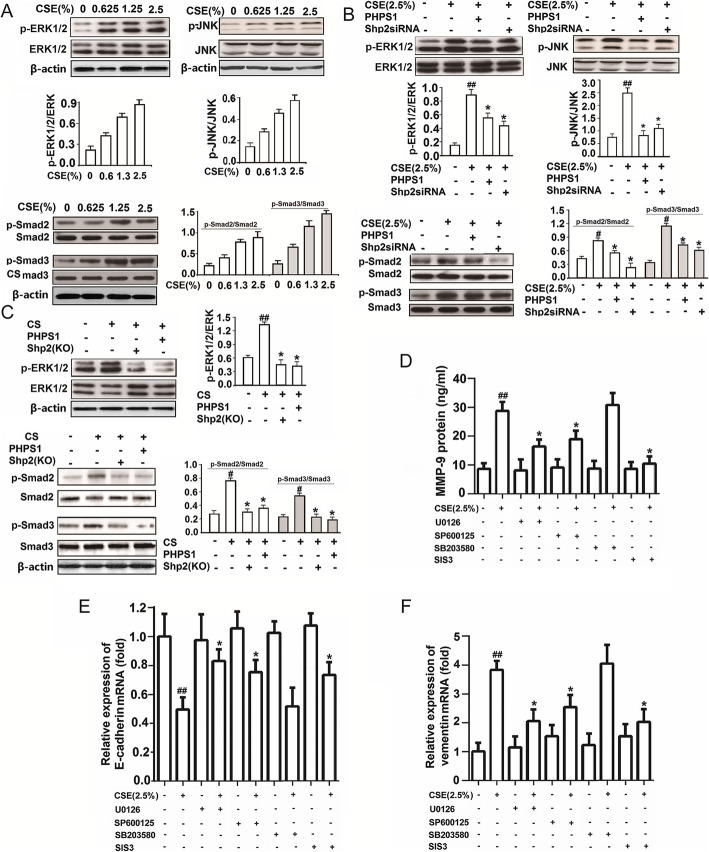
Fig. 7.
Genetic ablation of Shp2 in lung epithelial cells or pharmacological inhibition of Shp2 suppresses the CS- and CSE-induced expression of MMP-9 through MAPK/JNK/Smad signaling in lung tissues and in NCI-H292 cells. a Fifteen minutes of CSE incubation with indicated concentration induces phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK and Smad2/3 in a concentration dependent manner in NCI-H292 cells. n = 3 per group. b Shp2 inhibition by PHPS1 or knock down by siRNA attenuates the CSE-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK and Smad2/3 in NCI-H292 cells. n = 3 per group. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, compared with control (no treatment); *p < 0.05 compared with cells with CSE exposure. c Shp2 knock out in lung epithelial cells or inhibition by PHPS1 attenuates the CS-induced phosphorylation of ERK/1/2 and Smad2/3 in lung tissues. n = 3 per group. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, compared with control (no treatment); *p < 0.05 compared with cells with CSE exposure. d-f ERK1/2 inhibitor U0126 (10 μM), JNK inhibitor SB600152 (10 μM), P38MAPK inhibitor SB203580 (10 μM) and Smad2/3 inhibitor SIS3 (10 μM) attenuates the 24 h CSE (2.5%) induced MMP-9 protein production and vimentin mRNA expression, and reverses the 24 h CSE (2.5%) induced E-cadherin mRNA decreases in NCI-H292 cells. n = 3 per group. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, compared with control (no treatment); *p < 0.05 compared with cells with CSE exposure. At least three independent experiments in vitro were completed for each group assessment. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Statistical significance is determined by one-way ANOVA followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls test