Fig. 4.
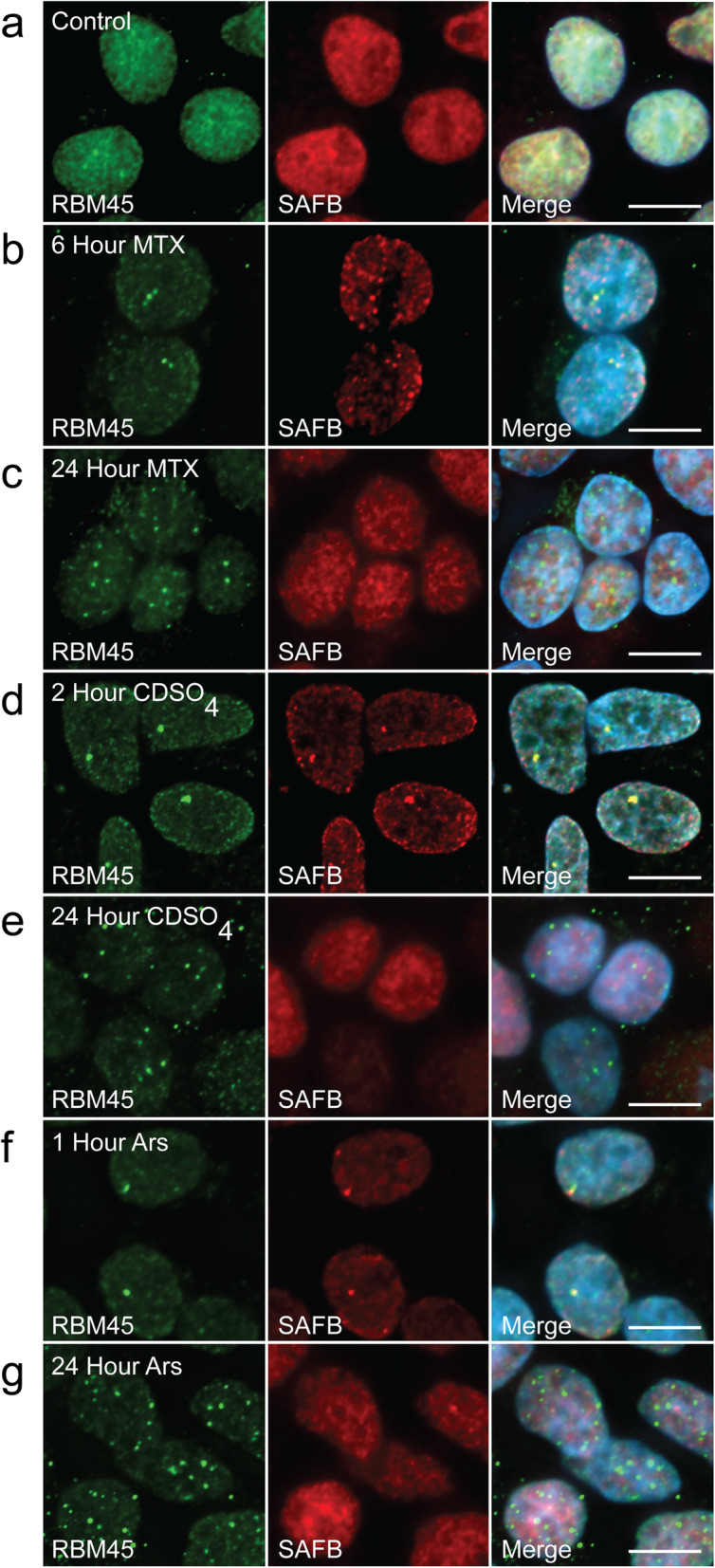
Chronic stress promotes RBM45 nuclear inclusion formation. HEK293 cells were treated with three separate cellular stressors for varying durations to examine the effects of chronic and acute cellular stress on the subcellular distribution of RBM45 and nuclear stress body (NSB) formation. a In untreated cells, the distribution of RBM45 is diffuse and nuclear and no SAFB-positive NSBs are visible. b Acute treatment (6 h) with the genotoxic stressor mitoxantrone (MTX; 5 μM) induces the formation of RBM45- and SAFB-positive NSBs. c Chronic treatment with MTX (24 h; 1 μM) leads to the formation of RBM45 inclusions via NSB formation. At 24 h, RBM45 nuclear inclusions are no longer positive for the NSB marker SAFB. (d and e) Similar results were obtained with acute (d) and chronic (e) treatment of cells with the oxidative stressor cadmium sulfate (CdSO4; 30 μM [acute] or 5 μM [chronic]) and the NSB marker SAFB. f and g Similar results were also obtained for acute and chronic treatment of HEK293 cells with sodium arsenite (Ars; 1 mM [acute; g] or 0.1 mM [chronic; h]). For all images, scale bar = 5 μm
