Figure 3.
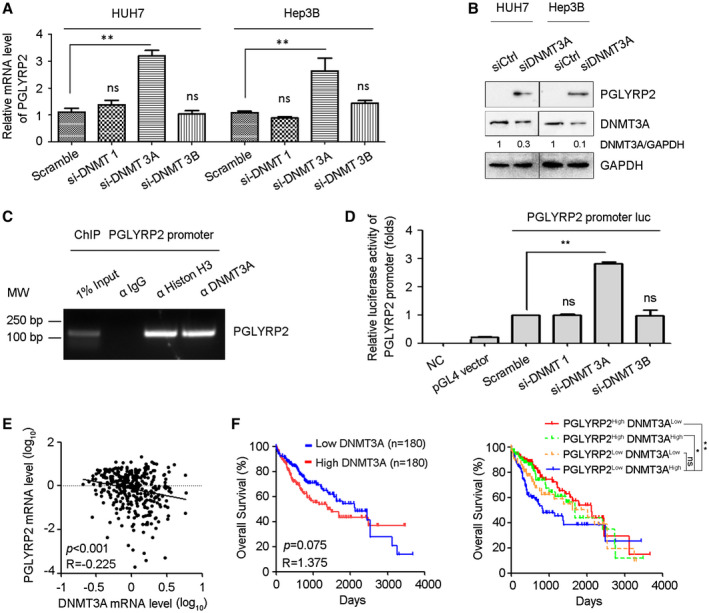
DNMT 3A mediates promoter hypermethylation of PGLYRP2 in HCC. (A) PGLYRP2 levels were examined in DNMT 1–silenced, DNMT 3A–silenced, or DNMT 3B–silenced Huh7 and Hep3B cells by real‐time PCR. The results are reported as mean ± SEM. (B) Western blotting results showed that knockdown of DNMT 3A in Huh7 and Hep3B cells significantly elevated the level of PGLYRP2. (C) The binding activity of DNMT 3A to the PGLYRP2 promoter was assessed by ChIP assay in Huh7 cells. (D) Relative luciferase activity in Huh7 cells transfected with plasmids of pGL4 vector, PGLYRP2 promoter luciferase reporter, scramble siRNA, DNMT 1 siRNA, DNMT 3A siRNA, or DNMT 3B siRNA, alone or in their combinations. The results are reported as mean ± SEM. (E) Confidence ellipse analysis showed that PGLYRP2 levels were inversely correlated with DNMT 3A expression in HCC tissues from TCGA‐LIHC. (F) Kaplan‐Meier analysis showed that the patients from TCGA‐LIHC who expressed low levels of DNMT 3A had a slightly longer OS (left panel), while patients with low DNMT 3A and high PGLYRP2 expression in tumors had a significantly improved OS compared to those in the high–DNMT 3A and low–PGLYRP2 expression group (right panel). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001. Abbreviations: GAPDH, glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase; IgG, immunoglobulin G; luc, luciferase; MW, molecular weight; NC, negative control; ns, not significant.
