Figure 1.
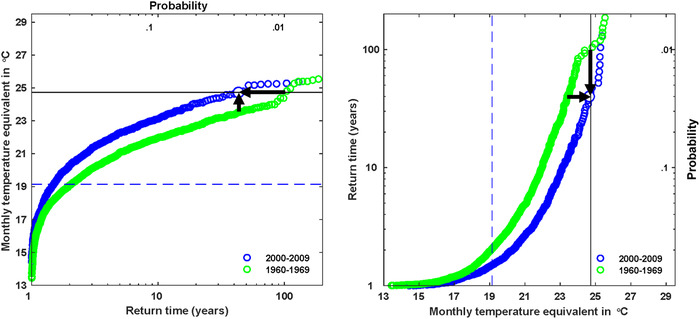
The effect of anthropogenic climate change on July heat waves over western Russia, motivated by the extreme heat wave of summer 2010. In both panels, the actual event magnitude is indicated with the solid black line and the July mean temperature during the 1960s with the dashed blue line, together with modeled estimates of the likelihood of exceeding a particular temperature threshold for both 1960s (green) and 2000s (blue) conditions, in terms of either probability or return time. The left panel shows magnitude versus probability, while the right panel shows probability versus magnitude. The two black arrows in each panel point to the observed event in the factual calculation. Anthropogenic climate change is seen to have increased both the magnitude and the probability of the heat wave. From Ref. 2, and adapted from Ref. 16.
