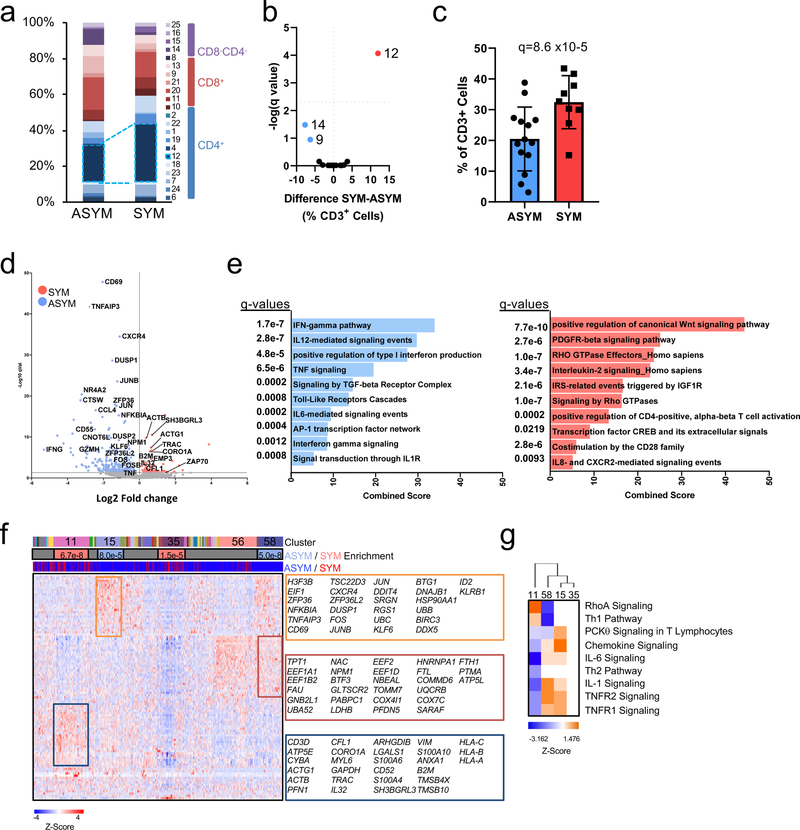
Figure 4. Dysregulation of CD4+ T cells associated with cerebrovascular events.
(a-c) Cohort 2 MC analyses on 23 patients stratified by asymptomatic (ASYM, n=14) and symptomatic (SYM, n=9). (a) Frequencies of MCs in plaque, sidebar (right) indicates MC T cell subtype(b) Volcano plot of MCs enriched in SYM (red) or ASYM (blue). (c) Frequency of T cells belonging to MC12 in plaques from ASYM and SYM patients. Values are mean ± SD. For (b, c) q values determined by two-sided multiple t-test with FDR=0.5% corrected using the Benjamini, Krieger and Yekuteli method. (d-g) Single-cell gene expression data of CD4+ T cells (n=1,200) from atherosclerotic plaques of both SYM (n=2) and ASYM (n=4) patients. (d) Volcano plot of the top 5000 Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs), determined by two-sided Welch’s T- Test and Benjamini-Hochberg correction, that were upregulated in SYM and ASYM(e) Pathway analysis of CD4+ T cell DEGs (n=5,000 genes) in plaques upregulated in SYM (right) and ASYM (left). The combined score metric corresponds to the P value (two-sided Fisher’s exact test) multiplied by the Z-score of the deviation from the expected rank, and q values determined by Benjamini-Hochberg correction. (f) Heatmap of hierarchically clustered top 100 variable genes across CD4+ T cells (n=1,200 cells) in SYM and ASYM patients. Rows: z-scored gene expression values; columns: individual cells. The top category of the heatmap shows identified cell clusters, the middle category indicates the cluster’s enrichment in SYM/ ASYM patients (p values determined by the two-sided binomial proportions test), and the bottom category indicates the cell’s origin from SYM or ASYM subjects. Boxes (right) list key genes found in corresponding clusters. (g) Canonical signaling pathway analysis of the top 5000 DEGs in the indicated cell clusters from plaques from SYM or ASYM patients.