Figure 5.
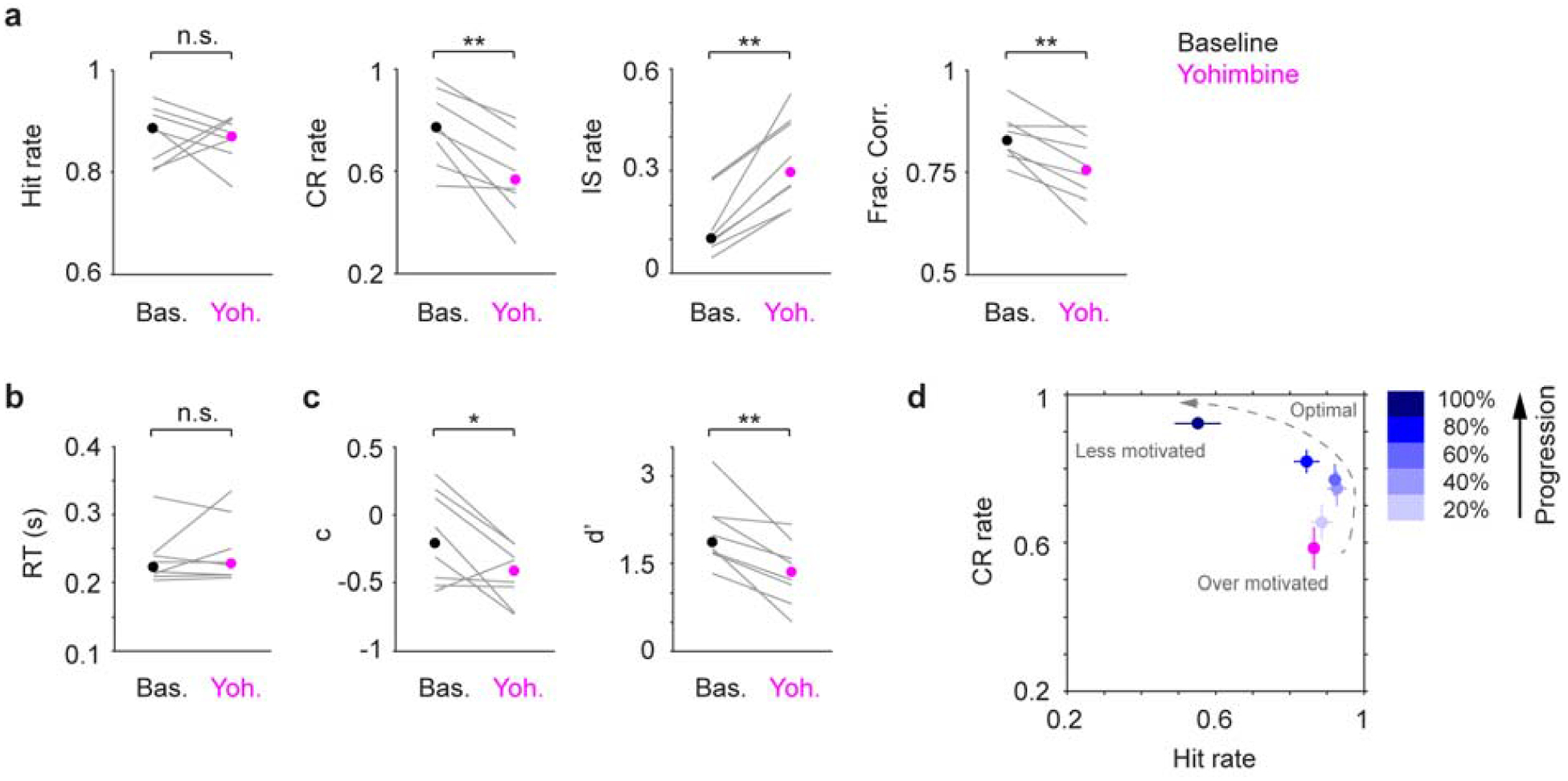
Systemic yohimbine treatment impairs tactile detection. a-c. Hit rate, CR rate, IS rate, Fraction Correct, RT, decision bias (c) and detection sensitivity (d’) for baseline (black dot, median) and yohimbine (magenta dot, median) sessions. Gray lines indicate individual consecutive two-day, baseline-yohimbine pairs. Hit rate, P = 1, Signed rank = 18; CR rate, P = 0.0078, Signed rank = 36; IS rate, P = 0.0078, Signed rank = 0; Frac. Corr., P = 0.0078, Signed rank = 36; RT, P = 0.84, Signed rank = 16; c, P = 0.039, Signed rank = 33; d’, P = 0.0078, Signed rank = 36. n = 8. d. CR rate vs. Hit rate trajectory showing yohimbine promotes impulsivity (high Hit rate and low CR rate), which coincides with mouse behavior at the beginning of normal baseline sessions. n.s., P > 0.05; * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01.
