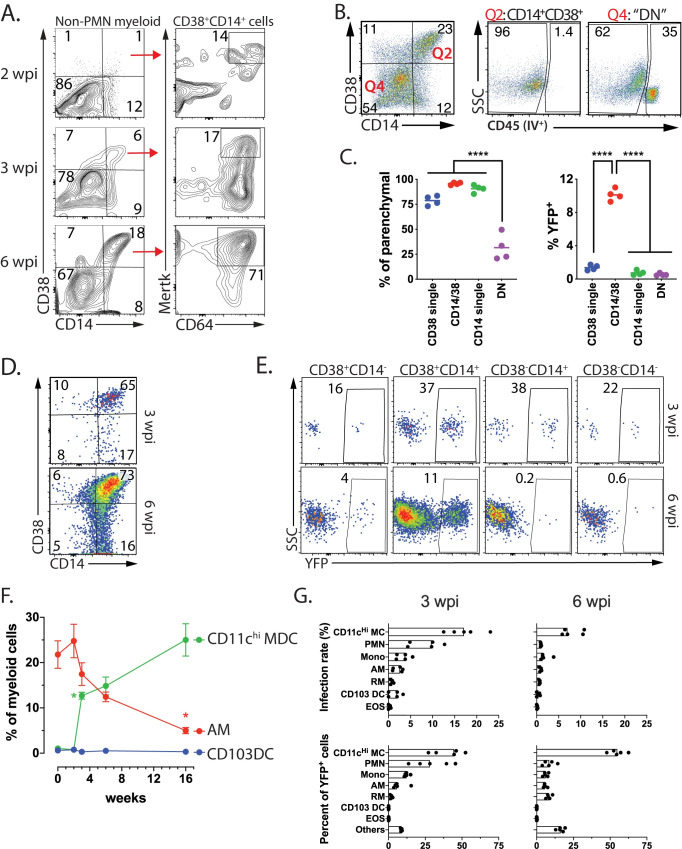
Fig 10. TP CD11cHi MDC are frequently infected by Mtb.
A. CD64 and MerTK expression by CD14+/CD38+ myeloid cells at 2, 3, or 6 weeks after Mtb infection. B. CD14+/CD38+ myeloid cells (i.e., “Q2”) are exclusively located in the lung parenchymal compartment while 35% of the CD14-/CD38- myeloid cells (i.e., “Q4”) are in the vasculature staining from intravenously administered anti-CD45 mAb. C. Quantification of parenchymal location of CD14+/CD38+ myeloid cells CD38 staining (from Fig 10B) (left) and the frequency of YFP+ cells among the four subsets (right). D. A majority of CD64+/MerTK+ myeloid “IM” cells express CD14 and CD38, 3 and 6 wpi. E. The frequency of YFP+ cells among CD64+/MerTK+ myeloid “IM” cells based on their expression of CD14 and CD38 expression at 3 and 6 wpi. F. The frequencies of CD11cHi MDC, AM and CD103 DC among myeloid cells after infection with Rv.YFP over time. Error bars, SD. *, p<0.05; t-test compared to the prior timepoint. Each time point represents five mice. G. The infection rate (%YFP+) for each of the seven myeloid cell types (top row) and the contribution of each cell type to the total YFP+ population (bottom row). Non-PMN myeloid cells (A-E) or total myeloid cells (F, G) were analyzed. Each time experimental group consists of five mice and is representative of at least two independent experiments.