Table 1.
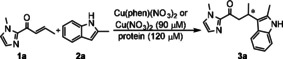
Vinylogous Friedel‐Crafts alkylation reactions catalyzed by MDR/Cu(II) or MDR/Cu(phen).
|
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Entry |
Catalyst |
Yield [%][a] |
ee [%][a] |
|
1 |
– |
<5 |
– |
|
2 |
Cu2+ |
22±7 |
– |
|
3 |
Cu(phen) |
43±2 |
– |
|
4 |
RamR |
5±6 |
8±6 |
|
5 |
Cu2+⊂RamR |
57±9 |
29±3 |
|
6 |
Cu(phen)⊂RamR |
21±13 |
34±7 |
|
7 |
CgmR |
6±3 |
10±21 |
|
8 |
Cu2+⊂CgmR |
52±12 |
13±3 |
|
9 |
Cu(phen)⊂CgmR |
30±3 |
15±1 |
|
10 |
QacR |
11±7 |
13±19 |
|
11 |
Cu2+⊂QacR |
78±11 |
34±3 |
|
12 |
Cu(phen)⊂QacR |
36±6 |
30±2 |
[a] Yields and ee's were determined by HPLC. Yields were calculated using 2‐phenylquinoline as internal standard. All the results listed correspond to the average of two independent experiments, each carried out in duplicate. Errors listed are standard deviations; [b] In all cases the (−) enantiomer was obtained in excess, as determined by comparison of the elution order in chiral HPLC to literature reports.29, 30