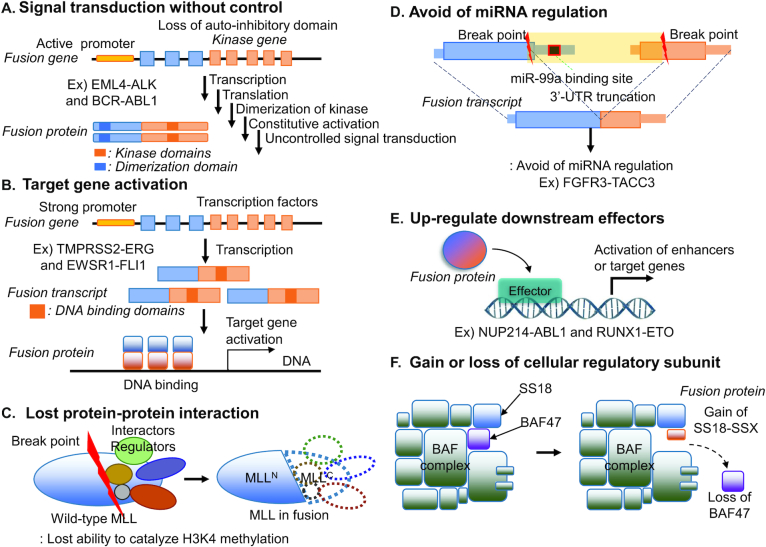
Figure 1.
Diverse tumorigenic mechanisms of FGs in cancer. (A) Signal transduction with control. The BCR with active promoter and dimerization domain is fused with a kinase domain of ABL1 and it leads to uncontrolled cell proliferation. (B) Target gene activation. If a transactivation domain of EWSR1 or tissue-specific androgen-responsive TMPRSS2 fused with a DNA-binding domain of FLI1 or ERG, it results in target gene activation. (C) Lost protein-protein interaction. MLL fusion proteins lose their interactions with important cellular. (D) Avoid of miRNA regulation. The 3′-UTR region of FGFR3 is truncated due to fusion gene, which can avoid the miRNA regulation. (E) Up-regulation of downstream effectors. Inhibition of STAT5, the downstream factor of NUP214-ABL1 led to leukemia cell death. (F) Gain/loss of cellular regulatory subunit. Due to SS18-SSX fusion gene in the BAF complex subunit, it affected the chromatin accessibility.