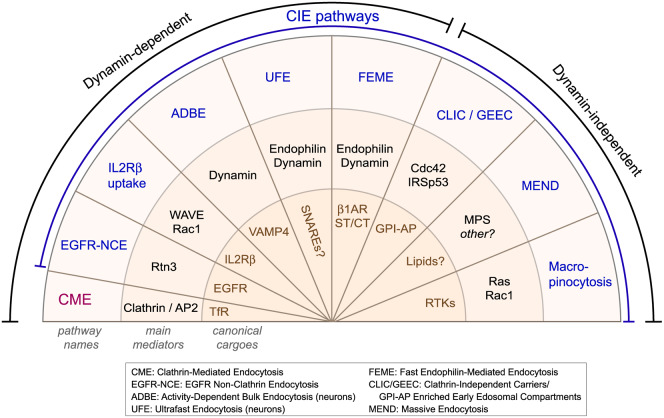
Figure 1. Clathrin-independent endocytic pathways.
Clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME) is the house-keeping pathway in resting cells. It is mediated by Clathrin and the tetrameric adaptor AP2 and its canonical cargo is Transferrin Receptor (TfR). Clathrin-independent endocytosis (CIE) is composed of Dynamin-dependent and Dynamin-independent pathways. EGFR Non Clathrin Pathway (EGFR-NCE) is regulated by Reticulon-3 (Rtn3) and internalizes Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) upon low doses of EGF. IL2Rβ uptake is a constitutive CIE pathway that internalizes IL2Rβ and γ under the control of Rac1 and WAVE. Activity-Dependent Bulk Endocytosis (ADBE) is controlled by Dynamin and internalizes VAMP4 and large patches of membranes upon high stimuli in neurons. Ultrafast Endocytosis (UFE) mediates the recycling of synaptic vesicle components (SNAREs?) in 50–100 ms following action potential in neurons. It is regulated by Endophilin, Dynamin and Synaptojanin. Fast Endophilin-Mediated Endocytosis (FEME) internalizes cargoes such as the β1-adrenergic receptor (β1AR) in 5–10 s following their stimulation, in an Endophilin- and Dynamin-dependent manner. Shiga toxin (ST) and cholera toxin (CT) can highjack FEME to enter cells, but can also use other CIE pathways. The Clathrin-Independent Carriers (CLIC)/GPI-anchored proteins (GPI-AP)-Enriched Early Endosomal Compartments (GEEC) pathway is a high capacity, Dynamin-independent, endocytic route, triggered by the extracellular clustering of GPI-AP, glycosylated proteins or lipids by Galectin-3. It is controlled by Cdc42, GRAF-1 and IRSp53. Massive Endocytosis (MEND) is the significant uptake of membrane induced upon Ca2+ and PI3 kinase signaling, mediated by membrane phase separation (MPS). Macropinocytosis is activated by strong and sustained Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTKs) signaling and form large (up to 20 µm) vacuoles upon the folding of membrane projections back to the cell surface.