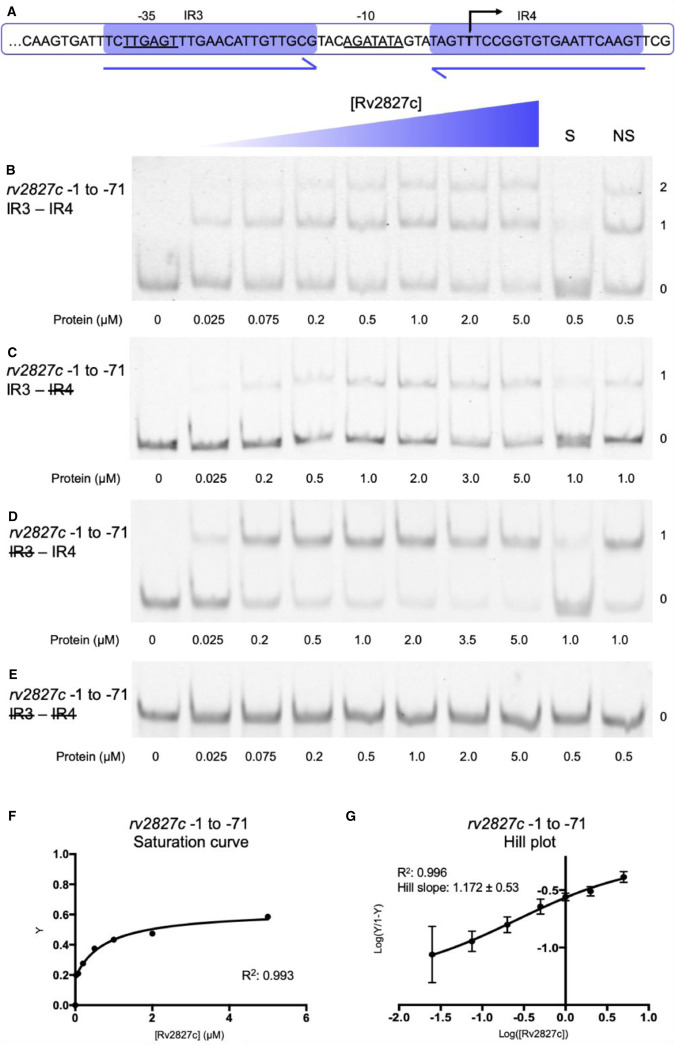
Figure 4. Rv2827c binds non-co-operatively to the IR3–IR4 region of the rv2827c–rv2826c promoter.
(A) Sequence level cartoon of the fluorescently labeled probe containing IR3–IR4, with −35, −10 and transcriptional start indicated. (B) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) of titrated Rv2827c with the probe in (A). (C) EMSA of titrated Rv2827c with the probe in (A) altered by replacing IR4 with polyC. (D) EMSA of titrated Rv2827c with the probe in (A) altered by replacing IR3 with polyC. (E) EMSA of titrated Rv2827c with the probe in (A) altered by replacing both IR3 and IR4 with polyC. For (B–E); protein concentrations are shown on each panel together with the binding events (0, 1 or 2); S — each experiment contained 100-fold excess of the specific unlabeled probe; NS — each experiment contained 100-fold excess of non-specific unlabeled probe; numbering −1 to −71 denotes the promoter region included in the probe, upstream of the translational start site in order to include all of IR4. (F) Fractional saturation curve plotted using the EMSA data of (B). (G) Hill plot using the EMSA data from (B). For (F) and (G), points are plotted from triplicate data and display mean values with standard error of the mean.