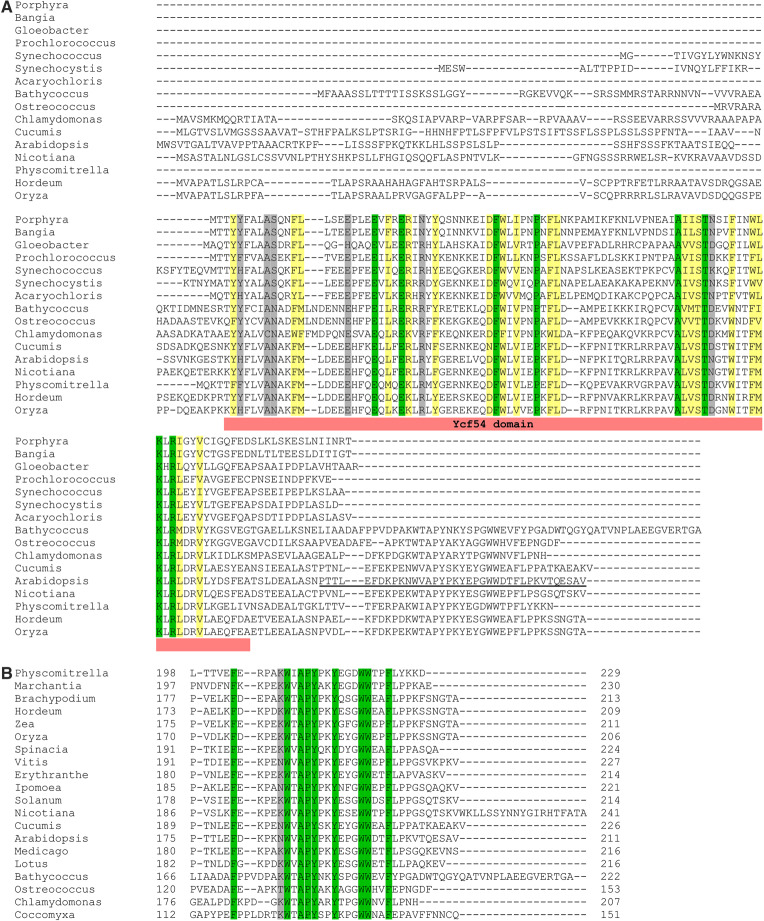
Figure 6. Amino acid sequence alignments of Ycf54 proteins.
Conserved, highly similar and similar residues are highlighted in green, yellow and gray, respectively. (A) Sequences are those from the primordial cyanobacterium Gloeobacter violaceus PCC 7421 (NP_923828); cyanobacteria, Prochlorococcus marinus MED4 (CAE19565), Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 (ACA98109), Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (BAA16792), Acaryochloris marina MBIC11017 (ABW27358); red algae, Porphyra purpurea (NP_053814), Bangia fuscopurpurea (AKE98807); green algae, Bathycoccus prasinos (XP_007514179), Ostreococcus tauri (XP_022839105), Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (XP_001691121); the moss Physcomitrella patens (XP_001756877); higher plants, Cucumis sativus (XP_004139926), Arabidopsis thaliana (NP_200633), Nicotiana tobacum (XP_016480530), Hordeum vulgare L. cv. Bonus (BAJ91312), Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica (XP_015628146). The conserved Ycf54 domain is indicated. The C-terminal 37 aa sequence deleted in the YCF54* mutant is underlined. (B) Sequence alignments showing the conservation of the C-terminal extensions present specifically in green algal and plant Ycf54 proteins. Additional green algal and plant Ycf54 sequences are included, which are from the green alga Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C-169 (XP_005642819); the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha (PTQ33664); higher plants, Brachypodium distachyon (XP_003557990), Zea mays (NP_001131876), Spinacia oleracea (XP_021852323), Vitis vinifera (XP_010650790), Erythranthe guttata (XP_012838088), Ipomoea nil (XP_019188624), Solanum lycopersicum (XP_004240451), Medicago truncatula (XP_013460499), Lotus japonicus (AFK37846). Full-length sequences were used for alignments but for clarity, only the C-terminal extension regions with the residue range indicated, are shown.