Fig. 1. Working principle and fabrication process of SEMAs.
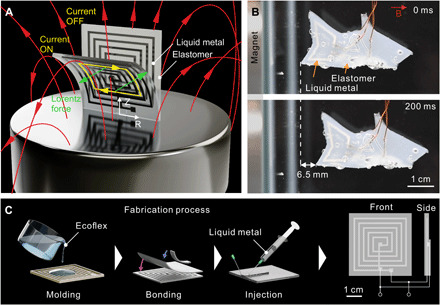
(A) Schematic working principle of a SEMA subjected to a current load in a magnetic field. (B) A swimming soft shark driven by SEMAs (tail and fins; movie S1). (C) Main steps of the SEMA fabrication: molding of the silicone elastomer, bonding to a sheet of elastomer to fabricate channels, and, last, injection of the liquid metal. Front and side layout of the finished square SEMA with both ends of the liquid metal connected to a control system. (Photo Credit: Michael Drack and Guoyong Mao/Johannes Kepler University Linz).
