Figure 1.
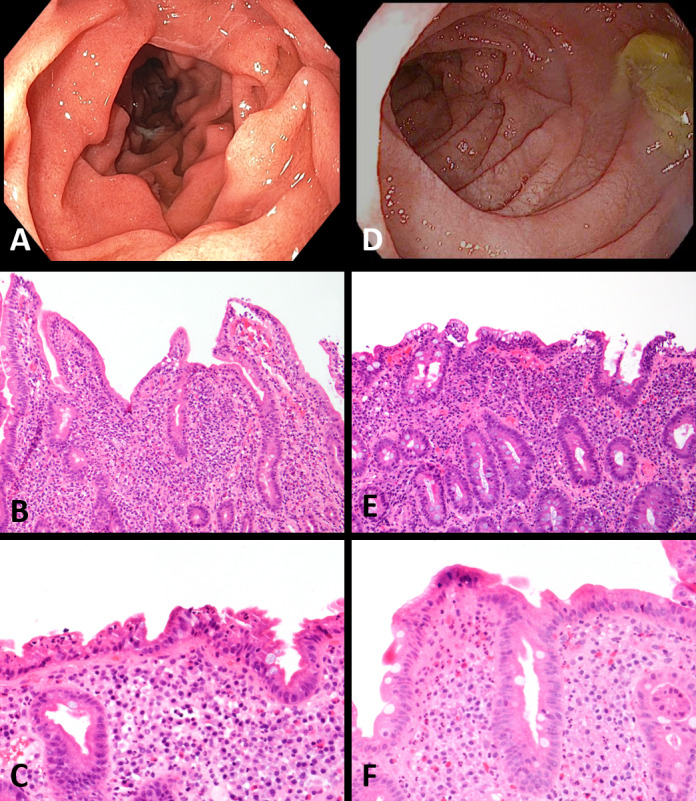
In a patient with immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-associated duodenitis, an endoscopic image of the duodenum reveals diffuse inflammation characterized by congestion, erosions, erythema, and granularity (A). On biopsy, routine H&E showed a markedly active neutrophilic duodenitis with mild-to-moderate villous blunting, marked expansion of the lamina propria, and only mildly increased intraepithelial lymphocytes (B, C). A patient with ICI-celiac disease (CeD) showed endoscopic findings of diffuse inflammation characterized by congestion, erythema, and friability (D). Biopsy of the duodenum showed a mildly active neutrophilic duodenitis with marked villous blunting and increased intraepithelial lymphocytes (E). Intraepithelial lymphocytosis, however, was not present in all ICI-CeD biopsies (F).
