Figure 3.
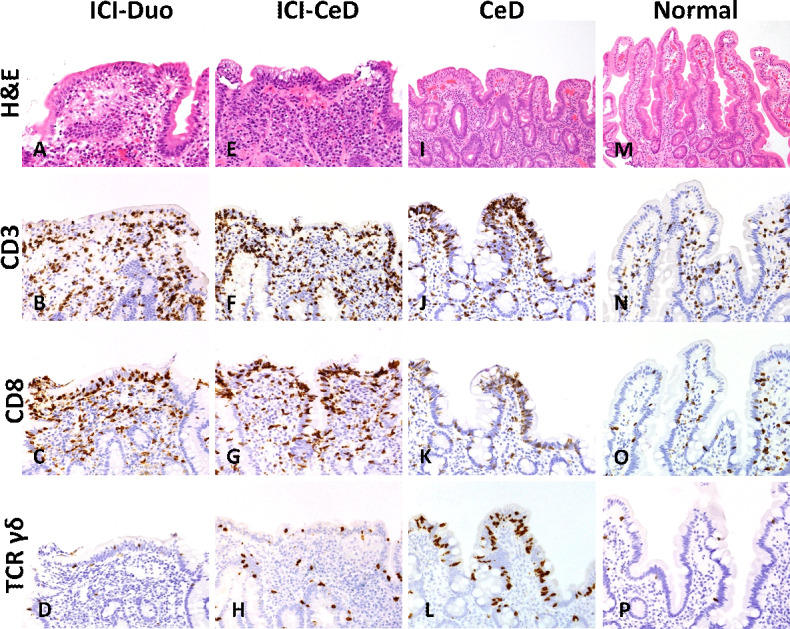
Representative images for (A–D) immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated duodenitis (ICI-Duo), (E–H) ICI-celiac disease (CeD), (I–L) CeD, and (M–P) normal duodenum are shown for routine H&E and immunostains for CD3, CD8, and T-cell receptor (TCR) γδ, respectively. In comparison to normal duodenum, ICI-Duo, ICI-CeD, and CeD show marked villous blunting, with a variably increased intraepithelial CD3+ CD8+ T cells. However, CeD is further characterized by a marked increase in intraepithelial γδ T cells compared with the other groups.
