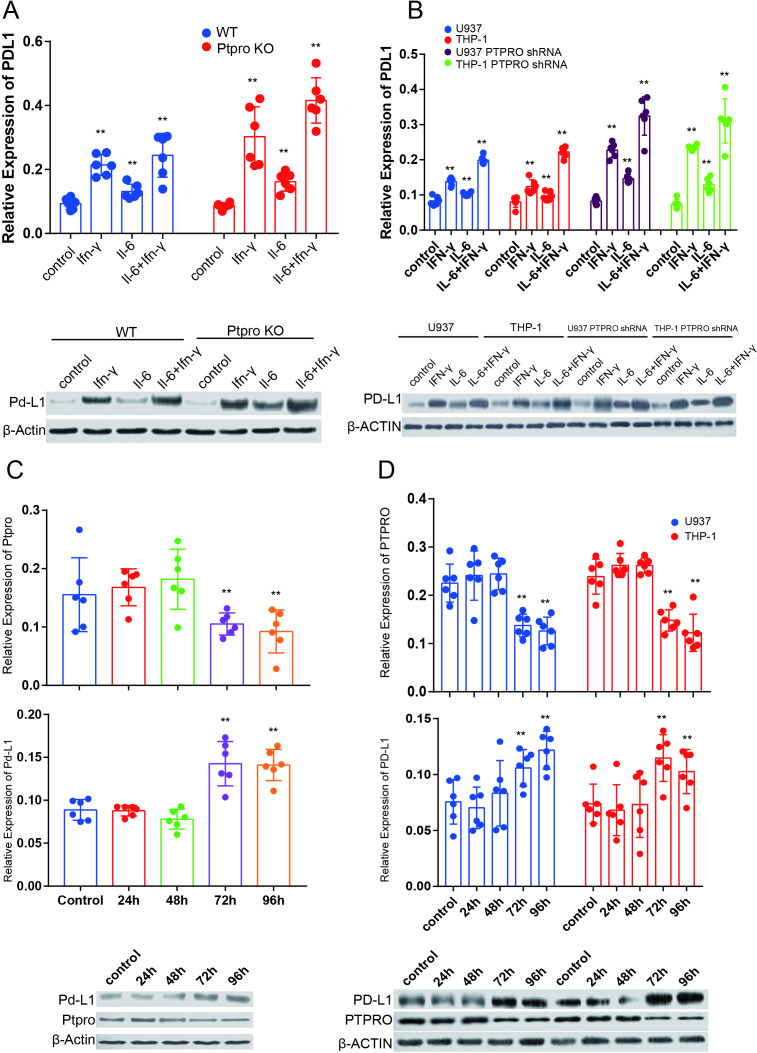
Figure 4.
IL-6 promotes PD-L1 expression in macrophage both directly and IFN-γ dependently by deregulating protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type O (PTPRO). (A) Macrophages isolated from wild-type (WT) and PTPRO KO mice were treated with IFN-γ (50 ng/mL), IL-6 (50 ng/mL), and IFN-γ+IL-6 (50 ng/mL) for 72 hours and the transcription and protein expression of Pd-L1 were determined by using real-time PCR and western blotting, respectively. (B) U937-, THP-1–, U937 PTPRO shRNA–, and THP-1 PTPRO shRNA–derived macrophages were treated with IFN-γ (50 ng/mL), IL-6 (50 ng/mL), or IFN-γ+IL-6 (50 ng/mL each), and the transcription and protein expression of PD-L1 were determined by real-time PCR and western blotting, respectively. (C) Macrophages isolated from WT and PTPRO KO mice were treated with IL-6, and the expression of PD-L1 and PTPRO was detected by real-time PCR and western blotting at different times after IL-6 treatment. (D) U937-, THP-1–, U937 PTPRO shRNA–, and THP-1 PTPRO shRNA–derived macrophages were treated with IL-6, and the expression of PD-L1 and PTPRO was detected by real-time PCR and western blotting at different times after IL-6 treatment. Each experiment was performed in triplicate. Data are presented as the mean±SEM and were analyzed by Student’s t-test (**p<0.01).