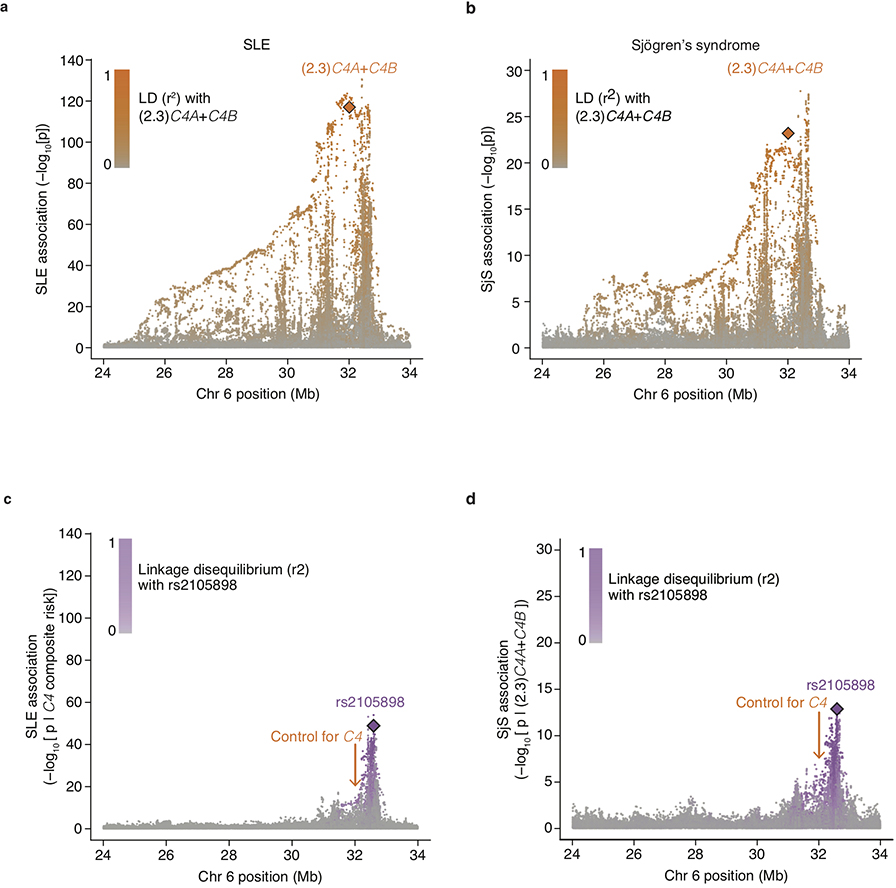
Extended Data Figure 3. Conditional association analyses for genetic markers across the extended MHC genomic region within the European-ancestry SLE and Sjögren’s syndrome (SjS) cohort.
(a) Association of SLE with genetic markers (SNPs and imputed HLA alleles) across the extended MHC locus within the European-ancestry SLE cohort (6,748 cases and 11,516 controls). Orange diamond: an initial estimate of C4-related genetic risk, calculated as a weighted sum of the number of C4A and C4B gene copies: (2.3)C4A+C4B, with the weights derived from the relative coefficients estimated from logistic regression of SLE risk vs. C4A and C4B gene dosages. This risk score is imputed with an accuracy (r2) of 0.77. Points representing all other genetic variants in the MHC locus are shaded orange according to their level of linkage disequilibrium–based correlation to this C4-derived risk score.
(b) As in a, but for a European-ancestry Sjögren’s syndrome (SjS) cohort (673 cases and 1,153 controls). The orange diamond here also represents (2.3)C4A+C4B, with this weighting derived from the relative coefficients estimated from logistic regression of SjS risk vs. C4A and C4B gene dosages
(c) Association of SLE with genetic markers (SNPs and imputed HLA alleles) across the extended MHC locus within the European-ancestry SLE cohort controlling for C4 composite risk (weighted sum of risk associated with various combinations of C4A and C4B). Variants are shaded in purple by their LD with rs2105898, an independent association identified from trans-ancestral analyses.
(d) As in c, but in association with a European-ancestry SjS cohort. Here a simpler linear model of risk contributed by C4A and C4B was used instead of a weighted sum across all possible combinations.