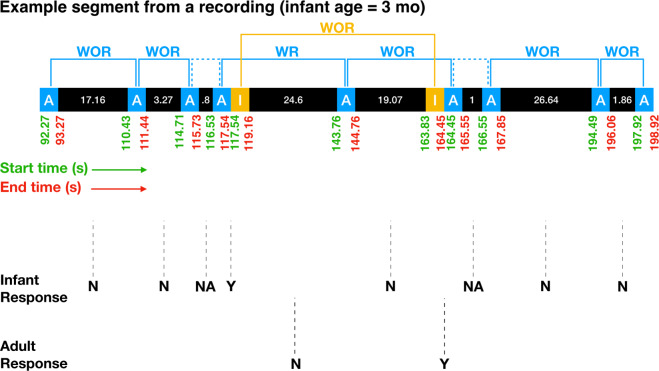
Figure 2.
Illustration of the automatic labelling scheme. Here, we use a small portion from a recording of an infant at age 3 months to illustrate the labelling scheme. The information in the top portion of the figure is provided by the LENA system; inter-vocalisation intervals, acoustic features, and response codes are computed automatically based on LENA-generated speaker labels and the original audio file. Adult vocalisations are in blue boxes while infant vocalisations are in yellow boxes. The start time of each vocalisation is indicated in green below the corresponding box, on the left, while the end time is in red and towards the right of the box. Inter-vocalisation intervals (in s) are given in black boxes between subsequent vocalisations, and the length of the box is indicative of the duration of the inter-vocalisation interval. For each infant/adult vocalisation, the receipt of a response (Y/N/NA) is indicated (dotted vertical line). An adult vocalisation is labelled as having been followed by an infant “response” (WR for “with response”; Y in the Infant Response row) if the onset of an infant vocalisation occurs within 1 s following the offset of the adult vocalisation, with no intervening adult vocalisation. The same logic applied for labelling whether adult “responses” followed infant vocalisations. If two adult vocalisations are separated by 1 s or less without an intervening infant vocalisation, then response to the first is NA. Adult vocalisation steps analysed in this study are indicated by the blue lines, with steps following a response labelled WR in blue, and steps following no response labelled WOR (for “without response”) in blue. Infant vocalisation steps are indicated by the yellow lines, with steps following a response labelled WR in yellow, and steps following no response labelled WOR in yellow. Dotted lines connecting vocalisations indicate that the corresponding inter-vocalisation interval was not analysed because it was less than or equal to 1 s with no intervening response. Analysed inter-vocalisation intervals were divided into WR and WOR depending on whether the first vocalisation in the sequence was followed within 1 s by a “response”.