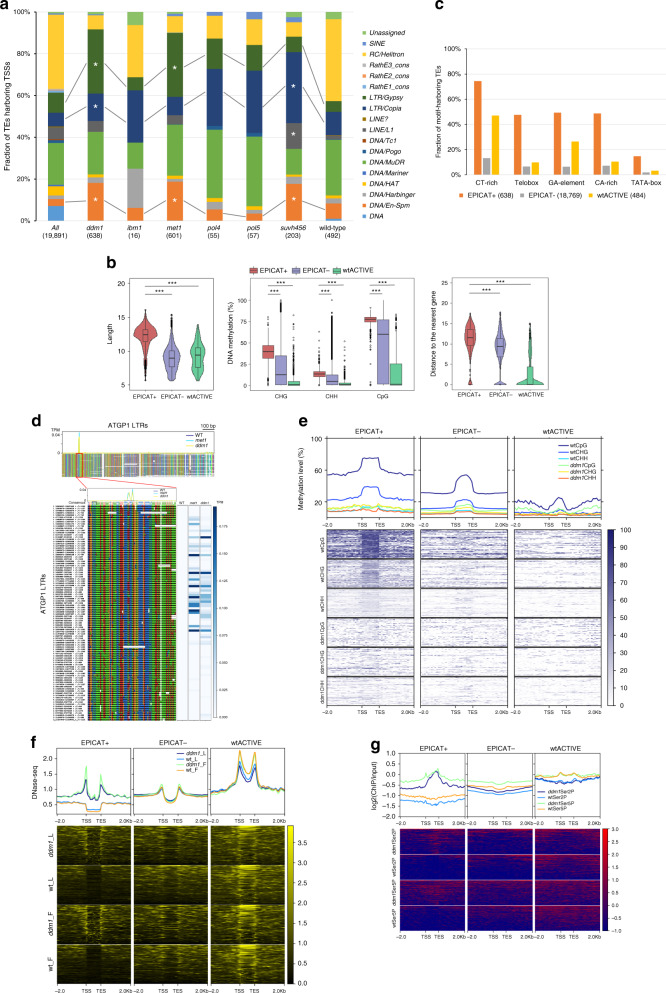
Fig. 5. TEs are a major genetic supplier of cryptic TSSs in the A. thaliana genome.
a Transposon families harboring the EPICATs. Shown are total numbers of TEs. All, wild-type: TEs in the A. thaliana genome and TEs harboring active TSSs in wild-type plants, respectively. *TE families enriched compared to the genome-wide average (p < 3e-04, Hypergeometric test). b Violin and/or boxplots showing the Length (left), DNA methylation (middle), and Distance to the nearest gene (right), of TEs harboring (EPICAT+), not harboring (EPICAT−) the EPICATs in ddm1, and harboring active TSSs in wild-type plants (wtACTIVE). ***p < 2.2e-16, two-sided Mann–Whitney test. c Fractions of TEs harboring consensus DNA motifs found at the ddm1-activated EPICATs. d Sequence alignment of representative LTRs of TEs belonging to the Gypsy ATGP1 sub-family. LTR sequences were aligned based on relative positions of cryptic TSSs detected by CAGE-seq. A, C, G, T nucleotides were colored in green, yellow, red, and blue. Putative TATA-box and YR-motifs are indicated by black box and red line, respectively. Relative positions and strand information of each LTRs in the genome are indicated (bottom left). Heatmaps of the normalized CAGE-seq data mapped to the LTRs using one replicate of each mutants are shown on the right side of the bottom panel. e DNA methylation of TEs in the wild-type (wt) and ddm1 backgrounds. TE lengths were normalized to 1 Kb and aligned by their two ends (indicated by TSS and TES). Methylation levels were calculated for non-overlapping 100 bp windows within TE body and surrounding region of ±2 Kb, and sorted by the average value of each row. f Chromatin accessibility at TEs in ddm1 and wild-type (wt) plants, given by DNase-seq data in flower (F) and leaf (L) tissues. Signals were calculated and presented as described in e, with the window size of 50 bp. g Ectopic recruitment of RNAPII Ser2P and Ser5P to TEs in the wild-type (wt) and ddm1 plants. Signals were calculated and presented as described in e, with the window size of 50 bp.