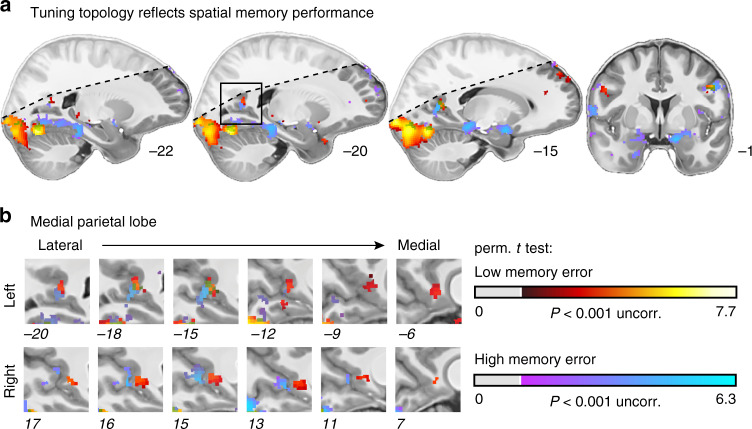
Fig. 4. Directional tuning topology reflects spatial memory performance.
Participants were split into two groups depending on their across-trial median memory error (2 × n = 10). a Tuning map: directionally tuned voxels were determined by testing model performance against zero on group level using a permutation-based t test with 1024 unique random possible shuffles. This procedure results in a minimal possible P value of 0.00098, precluding FDR correction. We therefore plot pseudo-T maps thresholded at P < 0.001 uncorrected for all basis sets at T1 resolution overlaid on the group-average T1 scan. Hot colors depict results for the low-memory-error group, cool colors for the high-memory-error group. Approximate MNI coordinates added. b Zoomed-in depiction of the medial parietal lobe/retrosplenial cortex (RSC). There is an anterior–posterior distinction in directional tuning in RSC as a function of spatial memory performance. Shaded regions fell outside the scanning field of view in at least one participant. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.