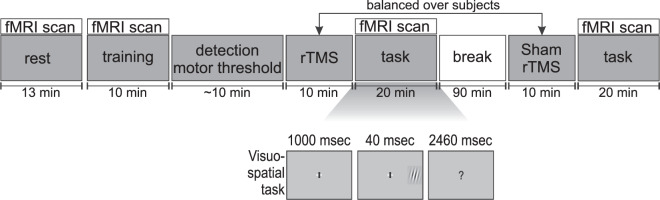
Figure 1.
Experimental design and task. Following a resting state measurement, training, and an assessment of TMS motor threshold, participants received either repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) or sham stimulation on the posterior parietal cortex, counterbalanced across subjects. The stimulation was followed by performing a visuospatial detection task inside the MRI scanner. Subjects were instructed to detect small Gabor patches that were presented either on the left, right, or both sides of the peripheral visual field. Following a break of 90 minutes and a period of, alternatively, TMS or sham stimulation, participants performed the task for the second time.