Figure 1.
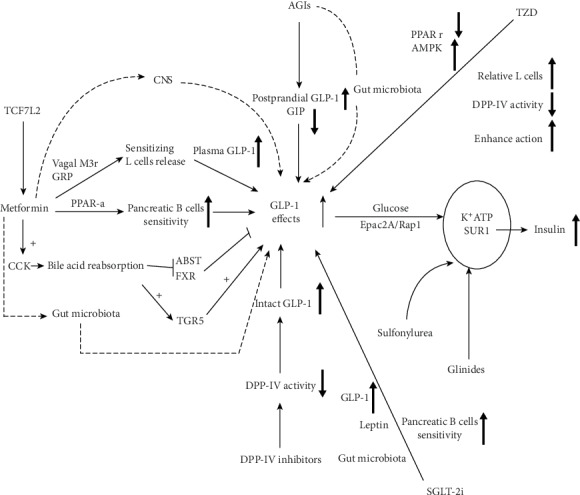
An overview of possible mechanisms of current major types of oral antidiabetic medications (OADs) on GLP-1 effect: including metformin, AGIs, TZD, SU, Glinides, SGLT-2i, and DPP-IV inhibitors. CNS: central nervous system; M3r: muscarinic receptor 3; GRP: gastrin-releasing peptide; PPAR-α: peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor; CCK: cholecystokinin; ABST: apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter; FXR: farnesoid X receptor; TGR5: Takeda G protein-coupled receptor; AGIs: α-Glucosidase inhibitors; DPP-IV: dipeptidyl peptidase-IV; TZD: thiazolidinedione; AMPK: Adenosine 5′-monophosphate- (AMP-) activated protein kinase; Epac2A: the exchange protein directly activated by cAMP; Rap1: Ras-associated protein 1; K+ATP: ATP sensitive potassium channel; SUR1: sulfonylurea receptor-1; SGLT-2i: sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor.
