Figure 2.
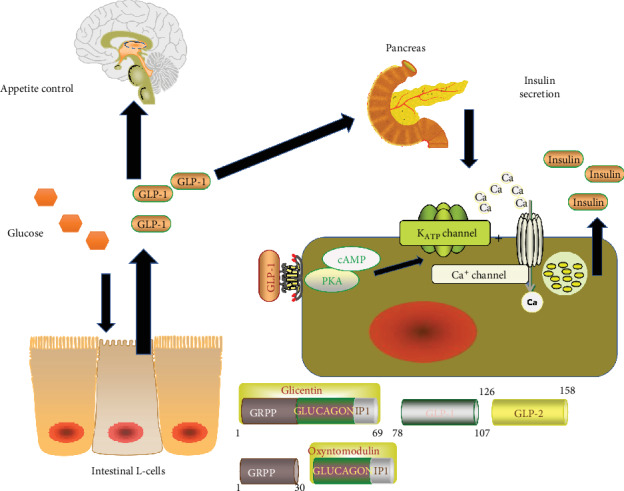
A brief review of the physiology of GLP-1. The intestinal GLP-1 can be secreted by the intestinal L cells under the stimulation of glucose. Then, the GLP-1 can bind to GLP-1 receptors of pancreatic β-cell. Its downstream action leads to the inhibition of ATP sensitive potassium channel, which results in the activation of calcium channel, and the accumulation of calcium in the cell promotes the secretion of insulin. On the other hand, the GLP-1 in the circulation can access the brain, which affects the appetite or energy control. cAMP: Cyclic Adenosine monophosphate; PKA: Protein kinase A; GRPP: Glicentin-related Pancreatic Polypeptide.
