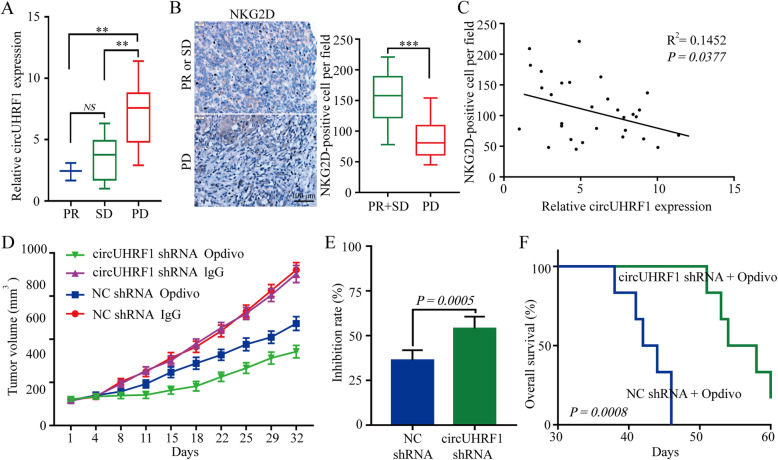
Fig. 7.
Higher levels of circUHRF1 correlate with resistance to anti-PD1 therapy in HCC patients. a Thirty patients were divided into PR, SD, and PD groups. The diagram shows circUHRF1 expression in each group. b Representative HCC cases were analyzed by IHC staining for NKG2D. c A negative correlation between miR-449c-5p and the number of NKG2D-positive cells was observed in the HCC tissues (R2 = 0.1452; P = 0.0377). d HCCLM3-NC shRNA or HCCLM3-circUHRF1 shRNA cells were subcutaneously injected into 4- to 6-week-old NOD/SCID mice, and when tumors reached a mean tumor volume of 100 mm3, NK (106) cells were injected intravenously through the tail vein, and mice were treated with IgG or Opdivo. The data are expressed as the mean tumor volume (the data are presented as the mean ± SD; n = 6). e The data are expressed as the percent of tumors with inhibited growth (the data are presented as the mean ± SD; n = 6). f Comparison of the overall survival curves for mice with high and low circUHRF1 expression in xenograft HCC tumors that were treated with Opdivo. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. NS: not significant