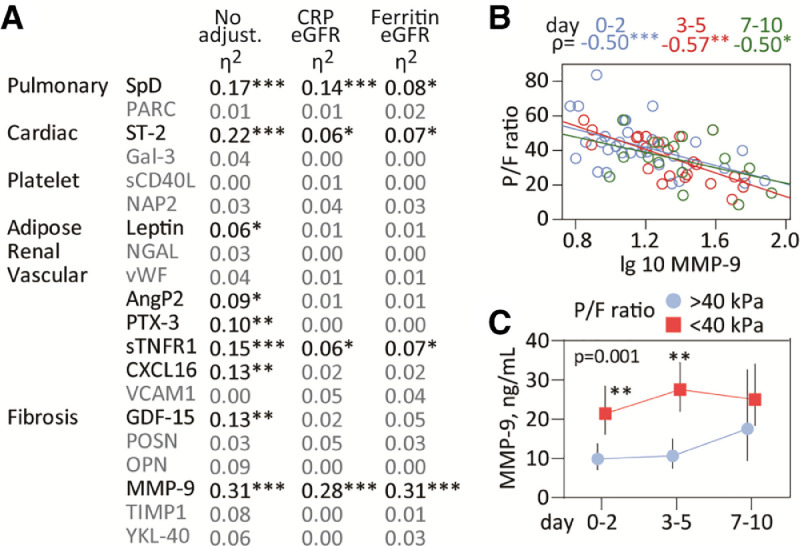
Fig. 1.
Inflammatory markers and respiratory failure during COVID-19 disease. A) Circulating markers measured in the study reflecting inflammation in relevant tissues or cells (pulmonary, adipose, cardiac, renal, platelets) or related to function (fibrogenesis, vascular inflammation). The table shows correlations between the P/F ratio and plasma markers during the course of the study. Partial eta2 is shown in unadjusted analysis (but with time as fixed factor) and following adjustment with eGFR and CRP or eGFR and ferritin. B) Spearman correlation between MMP-9 and P/F ratio at different time-points (day 0–2 blue, day 3–5 red, day 7–10 green) during the course of the study. C) Temporal course of MMP-9 during COVID-19 infection according to respiratory failure. Data are presented as back-transformed estimated marginal means with 95% confidence intervals from the mixed model analysis (see statistical methods) and the P-value for the group effect (i.e. respiratory failure) is given on the graph. *p<0.01, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. SpD, surfactant protein D; PARC/CCL18, pulmonary and activation-regulated chemokine; ST-2, suppression of tumorigenesis-2; Gal-3, Galectin-3 ; sCD40L, soluble CD40 ligand; NAP2/CXCL7, neutrophil activating peptide; NGAL, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; vWF, von Willebrand factor; AngP2, angiopoietin 2; PTX-3, pentraxin 3; sTNFR1, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1; CXCL16, C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 16; VCAM1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; GDF-15, growth differentiation factor; POSN, periostin; OPN, osteopontin; MMP-9, matrix metallopeptidase 9; TIMP1, tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase; YKL-40 also known as chitinase-3-like protein 1. . (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)