Figure 2.
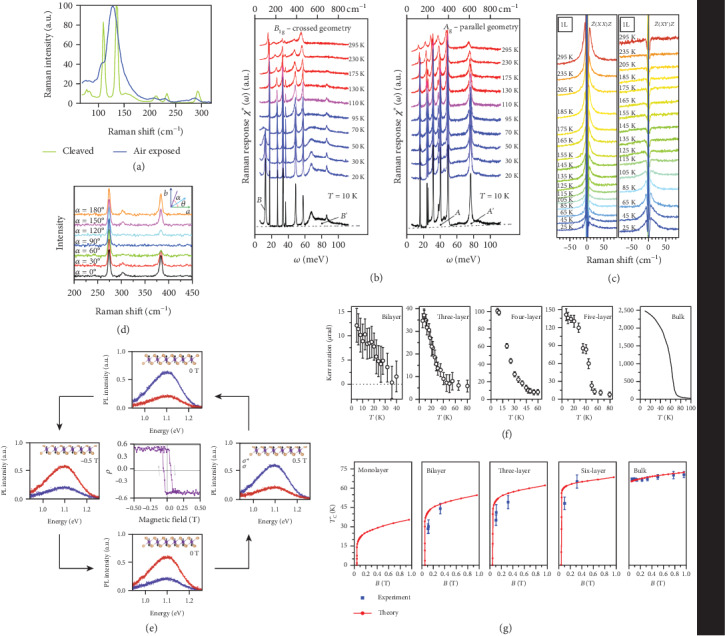
(a) Raman spectra of 30 nm Cr2Ge2Te6 under different conditions at 300 K. (b) Raman spectra of Ca2RuO4 with two magnetic geometries (B1g and Ag scattering) under various temperatures. (c) Low-frequency polarized Raman spectra of monolayer NiPS3. (d) Polarized Raman spectra of 10 nm MnPS3 with θ = 0. (e) Photoluminescence spectra of monolayer CrI3 for σ+ (red) and σ− (blue) circularly polarized photoluminescence with the application of an out-of-plane magnetic field at 15 K. The center panel is the plotting of circular polarization (ρ) dependence on the applied magnetic field. (f) Temperature-dependent Kerr rotation intensities of Cr2Ge2Te6 with varying thickness under a perpendicular field ~0.075 T. (g) Experimental (blue squares) and theoretical (red dotted lines) field-dependent TC of Cr2Ge2Te6 with varying thickness. Panel (a) is reproduced with permission from ref. [26], copyright 2016 2D Materials. Panel (b) is reproduced with permission from ref. [27], copyright 2017 Physical Review Letters. Panel (c) is reproduced with permission from ref. [29], copyright 2019 Nature Communications. Panel (d) is reproduced with permission from ref. [31], copyright 2017 ACS Nano. Panel (e) is reproduced with permission from ref. [33], copyright 2017 Nature Physics. Panel (f, g) are reproduced with permission from ref. [13], copyright 2017 Letter.
