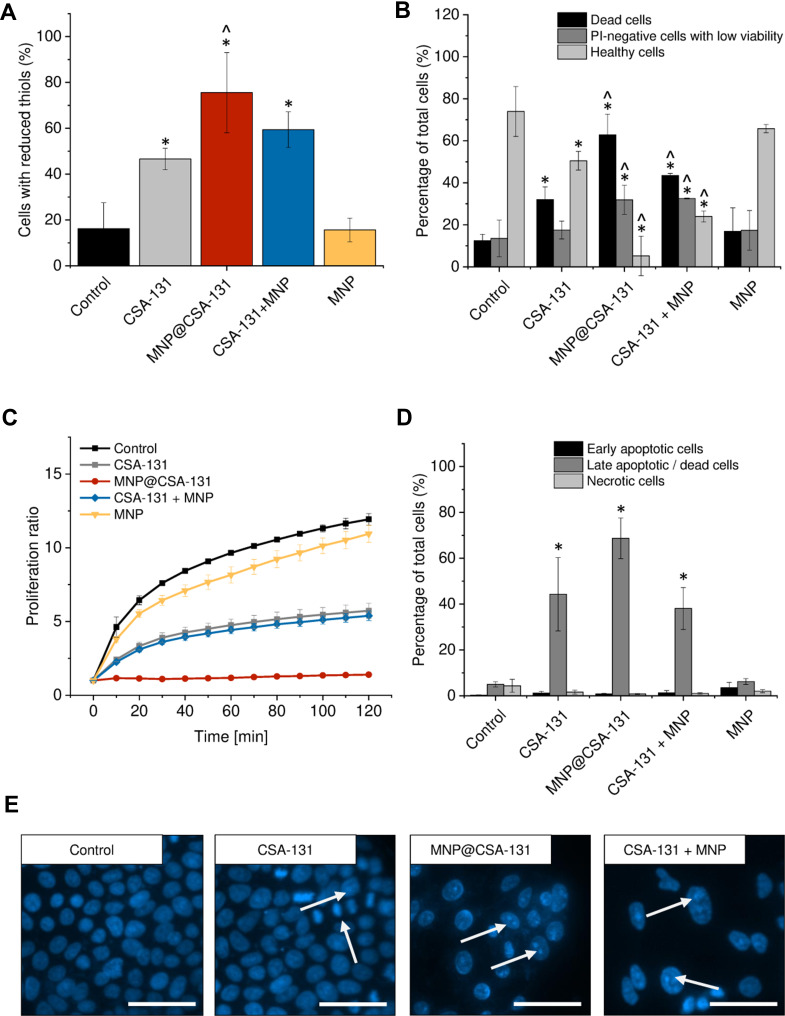
Figure 5.
Anticancer activity of ceragenin CSA-131 and ceragenin-containing nanoformulations against lung carcinoma A549 cells. Increase of intracellular levels of reduced thiols in A549 cells treated with CSA-131 (grey bar), MNP@CSA-131 (red bar), CSA-131+MNP (blue bar) and MNP (yellow bar) when compared to untreated control (0 µg/mL; black bar) (A). The percentages of dead cells (black columns), PI-negative cells with low viability (dark grey columns) and healthy cells (light grey columns) in lung carcinoma cells treated with CSA-131, MNP@CSA-131, CSA-131 and MNP or naked MNPs (B). The proliferation of cancer cells treated with CSA-131 (grey squares), MNP@CSA-131 (red circles), CSA-131 + MNP (blue diamonds) and MNP (yellow inverted triangles) when compared to untreated control (black squares) estimated using resazurin-based fluorimetric method (C). Induction of apoptosis in A549 cells by CSA-131 and its magnetic derivatives (D). Percentage of early apoptotic (black columns), late apoptotic/dead cells (dark grey columns) and dead cells (light grey columns). For the purpose of the clarity of the presented data, live cells (Annexin V-negative and 7-AAD-negative) were not presented in the provided figures. Morphological alternations in nuclei of A549 cells upon treatment with CSA-131, MNP@CSA-131 and CSA-131 + MNP when compared to uncreated cells (E). White arrows indicate treatment-induced morphological changes in nuclei of treated cells. All experiments were performed using agents at a concentration of 10 µg/mL for 24 h. (A–D) demonstrate results from 3 to 6 individual experiments ± SD, for panel E results from one representative experiment are shown. * and ^ indicate statistical significance (p-value <0.05) when comparing to control cells (0 µg/mL) and CSA131-treated cells, respectively. Scale bar ~50 µm.