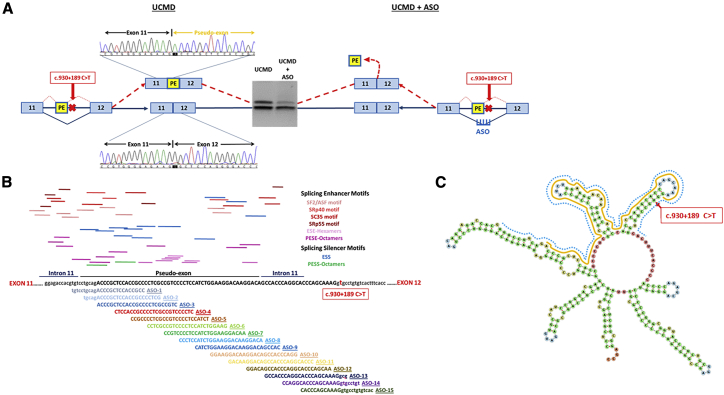
Figure 1.
Exon-Skipping Strategy Using Antisense Oligonucleotide
(A) The deep intronic mutation c.930+189C > T in COL6A1 creates a cryptic splice donor site responsible for the insertion of an in-frame pseudo-exon (PE) between exons 11 and 12 in the mature transcripts, as confirmed by PCR and Sanger sequencing. The exon-skipping strategy designed to target the c.930+189C > T mutation to skip the PE is illustrated. (B) Schematic representation of PE and its flanking sequences. The top panel shows the potential splicing enhancer and splicing silencer motifs predicted by the Human Splicing Finder (http://www.umd.be/HSF/). The bottom panel illustrates the 15 ASOs designed to anneal to the PE and its flanking 5′ and 3′ splice sites. (C) M-fold of PE and its flanking 5′ and 3′ sites using RNAfold web server (http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at//cgi-bin/RNAWebSuite/RNAfold.cgi). The PE is highlighted in yellow, and the region recognized by ASOs is indicated in blue.