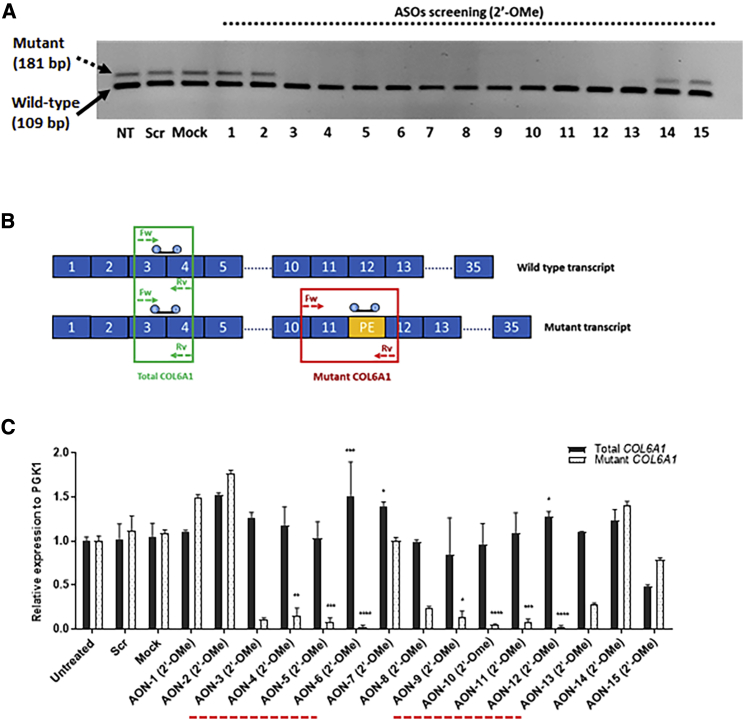
Figure 2.
Evaluation of ASOs Specificity and Efficiency in Pseudo-Exon Skipping at the RNA Level
(A) Gel electrophoresis of PCR products amplified in RNA samples isolated from UCMD fibroblasts treated with ASOs at 20 nM for 24 h with Lipofectamine transfection. (B) Schematic representation of quantitative real-time PCR assay. Two sets of primers with specific probes were used in the analysis. One set of primers with a specific probe complementary to the pseudo-exon (PE) to exclusively amplify the mutant transcripts. Another set of primers to amplify the total COL6A1 transcripts, including both wild-type and mutant transcripts. (C) Quantitative real-time PCR was performed in RNA samples collected from UCMD fibroblasts treated with 20 nM ASOs after 24 h of transfection, using specific primers and probes. The two regions, where ASOs are capable of efficiently skipping the PE from the mutant transcripts, are underlined by a dashed line in red. Data were normalized to untreated samples and analyzed by one-way ANOVA and post-Bonferroni test. Data are presented as mean ± SD (∗p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001).