Figure 1. MYC Interacts with AURKB.
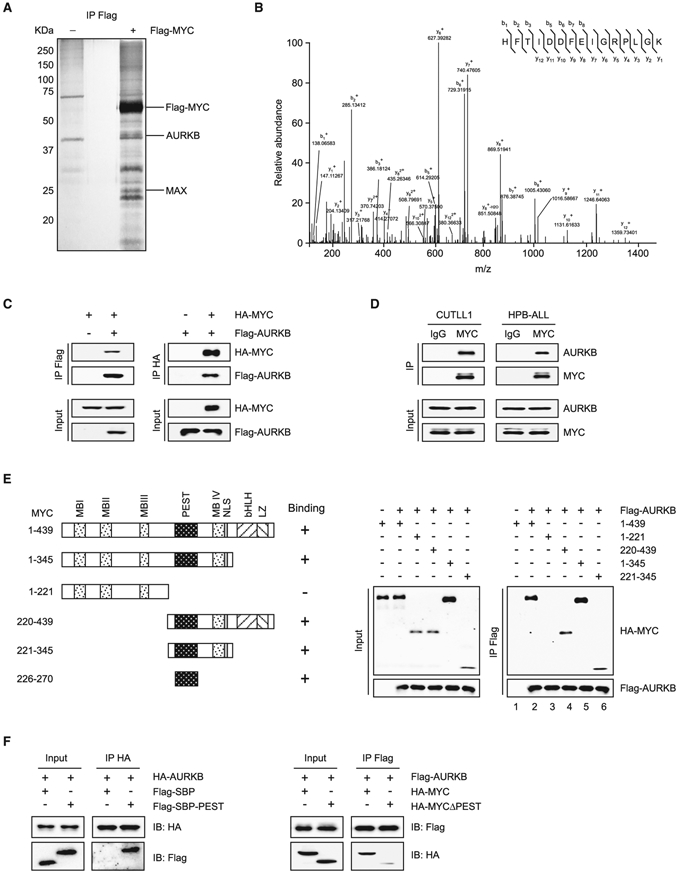
(A) Purification of MYC and its interacting partners. Total protein extract from Jurkat cells expressing Flag-tagged MYC or vector was subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag beads. Eluted proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver staining.
(B) Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of the Flag-MYC-associated peptides corresponding to AURKB.
(C) Lysates of 293T cells overexpressing Flag-AURKB and/or HA-MYC were subjected to reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) to detect protein interaction.
(D) CUTLL1 and HPB-ALL cell lysates were subjected to co-IP and immunoblot to detect endogenous MYC and AURKB interaction.
(E) Schematic presentation of various human MYC truncations used in AURKB-binding assays (left). Lysates from 293T cells overexpressing Flag-AURKB and/or various HA-MYC truncations were subjected to co-IP and immunoblot (right).
(F) Co-IP of HA-AURKB and Flag-tagged streptavidin-binding peptide (SBP)-fused MYC PEST domain (left), or Flag-AURKB and HA-MYCΔPEST (right) from lysates of 293T cells overexpressing respective tagged proteins.
See also Table S1.
