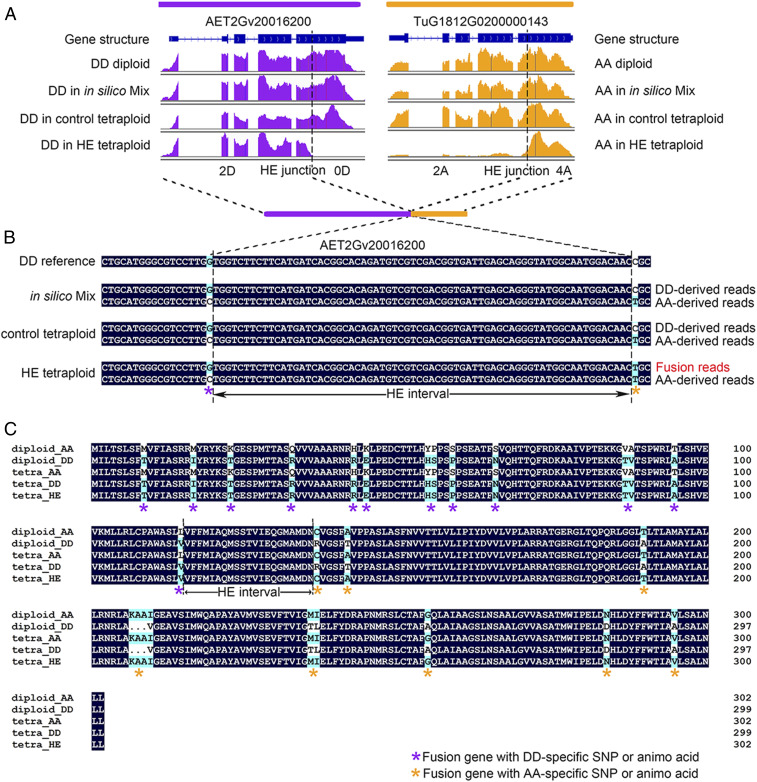
Fig. 5.
Gene fusion between HE-related homoeologous gene pairs. (A) IGV illustration of a homoeologous fusion event based on RNA-seq reads depth. Each track (from up to down) represents the transcript structure and gene expression profile in diploid, in silico tetraploid, control tetraploid, and HE-related tetraploid, respectively. Orange and purple indicate the profile of the A and D subgenome gene, respectively. The position of the HE junctions were marked as dashed lines. The combination of number and letter flanking the HE junction represent the copy number of a given subgenome in HE-related tetraploid (2A indicating two copies of A subgenome). Note the HE-related tetraploid exhibits truncated expression pattern. (B) Validation of fusion transcript based on diploid-specific SNP method. The tracks represent the consensus sequencing reads in in silico mix tetraploid, control tetraploid, and HE-related tetraploid. Nucleotides without black background indicate high-confident SNPs between AA and DD diploid and were used for genotyping the sequence reads. The asterisks in different colors under SNP positions indicate the origin of SNP (orange for A subgenome and purple for D subgenome) in fusion read. Regions between adjacent asterisks of different colors represent HE junction intervals. (C) Predicted amino acid sequence of fusion transcript by ORFfinder (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/) based on Sanger sequencing. Amino acids without black background indicate high-confidence variants between AA and DD diploids. The asterisks in different colors indicate the parental origin of the amino acid involved in the HE region (orange for A and purple for D) in the new predicted fusion protein. The region between adjacent asterisks of different colors represents the HE junction interval. Other similar cases of HE-related gene fusion events are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S7.