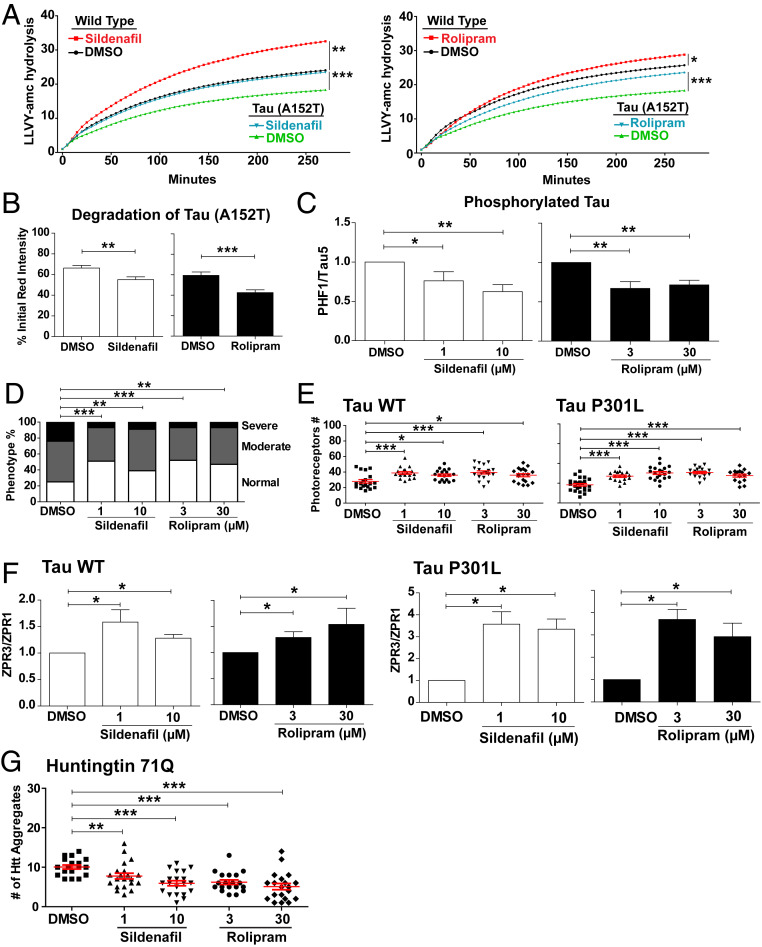
Fig. 5.
Sildenafil and rolipram treatment stimulate proteasome activity and reduce the levels of toxic proteins, cell death, and morphological abnormalities in zebrafish models of neurodegenerative diseases. (A) Addition of sildenafil to raise cGMP or rolipram to raise cAMP increased proteasome activity in WT fish and in fish overexpressing Dendra-tau-A152T. Proteasomal peptidase activity in fish overexpressing Dendra-tau-A152T was less than in control fish (35). The proteasomes’ chymotrypsin-like activity in fish lysates was measured using Suc-LLVY-AMC (n = 15 per group) after a 1-d treatment. Data represent mean values ± SEM here and below. Two-way ANOVA test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. (B) Sildenafil and rolipram treatment for 6 h increased the rate of tau clearance (n = 50 neurons per group). In vivo tau clearance of photoconverted “red” Dendra-tau was measured within individual neurons in the spinal cord. The measurement of the intensity of the photoconverted Dendra-tau signal at 6 h relative to initial red intensity reflects the clearance of tau protein. Two-tailed unpaired t test. **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. (C) The levels of hyperphosphorylated tau relative to total tau in Dendra-tau-A152T fish decreased after treatment with sildenafil or rolipram (n = 10 per group). The accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau is one of the hallmarks of tauopathies. Representative western blots shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S10A. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01. (D) Exposure to sildenafil and rolipram for 2 d ameliorates the morphological defects in Dendra-tau-A152T fish. Both treatments increased the percentage of larvae with normal phenotypes and reduced the proportion of deformed larvae (n = 100 per treatment group). χ2 test with confidence interval 95%. **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. (E) Quantification of photoreceptors from images of sections through the central retina (n ≥ 16 per group) showed that both sildenafil and rolipram increased the survival of photoreceptors above levels in siblings treated with DMSO. Representative images shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S10B. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *P ≤ 0.05, ***P ≤ 0.001. (F) Sildenafil or rolipram treatment reduce the degeneration of rod photoreceptors in Rho::EGFP-TauWT and Rho::EGFP-TauP301L zebrafish larvae. Densitometry of western blots for the major rod photoreceptor protein rhodopsin (ZPR3) relative to the loading control arrestin (ZPR1) from three independent experiments (n = 10 per group). Representative western blots used for quantification are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S10C. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *P ≤ 0.05. (G) In Rho::EGFP-HD71Q transgenic fish, in which the expression of the mutant form of huntingtin exon 1 (71Q) leads to aggregate formation and degeneration of rod photoreceptors sildenafil and rolipram treatment decreased the number of huntingtin aggregates below the levels in the control (DMSO-treated) group. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test. **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001.