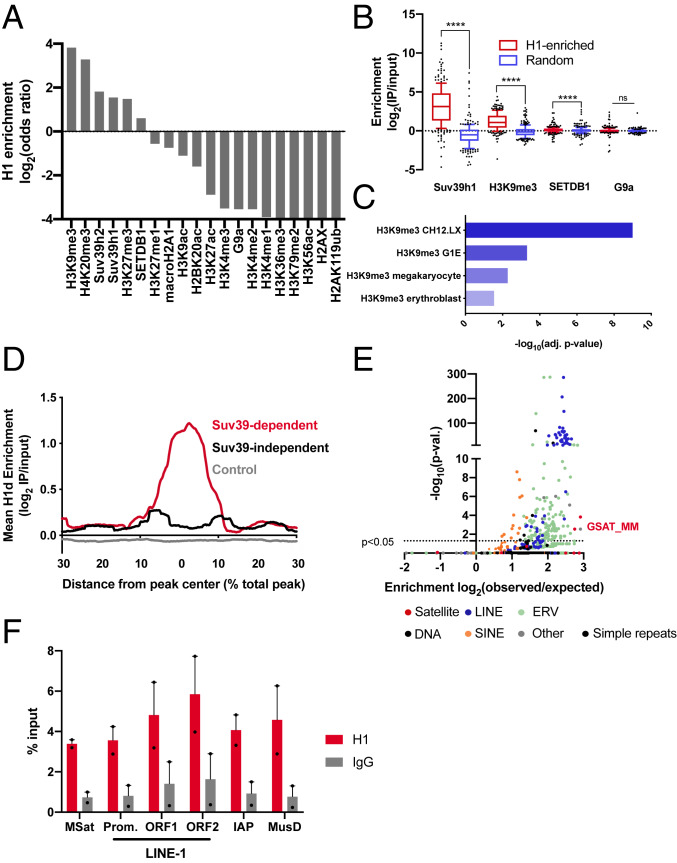
Fig. 1.
H1 is enriched within constitutive heterochromatin silenced by Suv39h1/2. (A) Overlap of H1d and histone posttranslational modifications or chromatin proteins in mESCs. ChIP-seq data for a number of histone PTMs and chromatin factors in mESCs was analyzed by ISOR to detect enriched regions. The overlap of H1d-enriched domains with each factor or modification is expressed as a log2(odds ratio). (B) The enrichment of Suv39h1, H3K9me3, SETDB1, and G9a within H1-enriched domains was compared to matched control genomic regions of equal size and number. Enrichment is expressed as log2(IP reads/input reads). (C) Significantly enriched histone posttranslational modifications in H1-enriched domains. H1-enriched ISOR regions (P < 0.01; ES >0.5) were analyzed by Enrichr (31) to detect significant overlaps with histone posttranslational modification ChIP-seq datasets. (D) H1 enrichment in Suv39-dependent, Suv39-independent, and control domains. Suv39-dependent and -independent H3K9me3 domains were determined (SI Appendix, Fig. S1 A and B), and the enrichment of H1d within these domains was analyzed using HOMER. Due to variable domain sizes, the x-axis is displayed as a percent of total peak length from the center. (E) Overlap of H1-enriched domains and repetitive elements genome-wide. H1 ISOR domains were analyzed by HOMER, and enrichment is expressed as log2(observed/expected) overlap. (F) Enrichment of H1a at repetitive elements. ChIP-qPCR was performed on fixed chromatin from ES cells using H1a and control IgG antisera. Enrichment is expressed a percentage of input DNA fragment recovered. ns, not statistically significant; *P ≤ 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to test for significance in B.