Figure 4. Depletion of monocytes/macrophages by INCB3344 and liposomal clodronate unmasked the anti-allodynic effect of local sympathectomy in paclitaxel-treated mice.
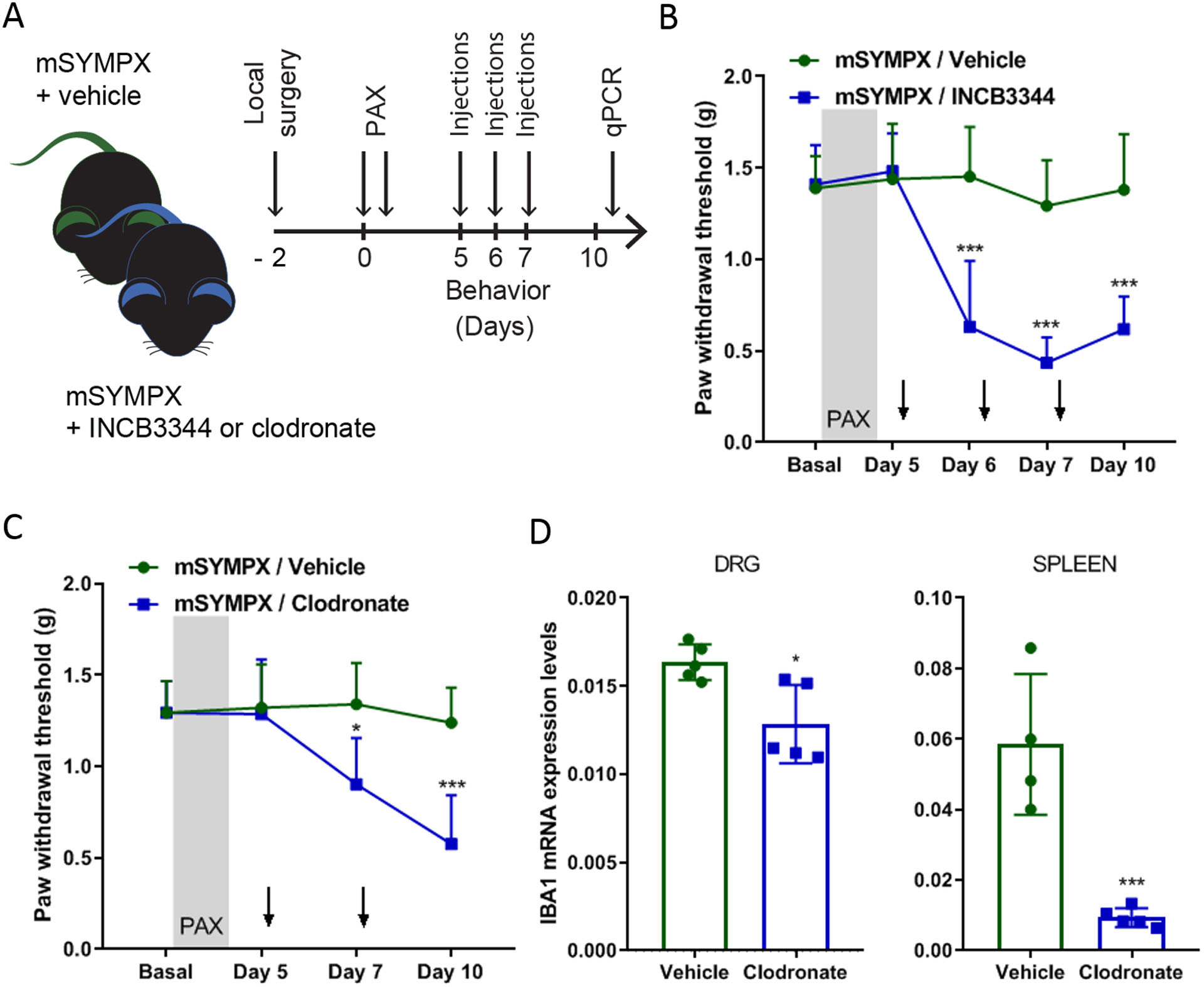
(A) Schematic illustration of the experiment showing the timeline of local microsympathectomy (mSYMPX), injections of paclitaxel (PAX), injections of INCB3344 (intravenously on day 5, 6, and 7) or liposomal clodronate (intraperitoneally on day 5 and 7), and behavioral and transcriptional (qPCR = real-time quantitative RT-PCR) assays. (B) Time course of paclitaxel-induced mechanical allodynia tested in ipsilateral hind paws in male mice treated with a vehicle control and INCB3344 (n=5 male mice/group, two-way ANOVA showed significant difference between mSYMPX –INCB3344 and -vehicle groups, Group × Time interaction: F4,32 = 10.14, p < 0.001; Bonferroni post hoc analysis revealed a significant difference between groups on day 6, 7 and 10. ***p < 0.001). (C) Time course of paclitaxel-induced mechanical allodynia tested in ipsilateral hind paws in male mice treated with a liposomal vehicle control and clodronate (n=5 male mice/group, two-way ANOVA showed significant difference between mSYMPX -clodronate and -vehicle groups, Group × Time interaction: F3,24 = 4.12, p = 0.017; Bonferroni post hoc analysis revealed a significant difference between groups on day 7 and 10. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001). (D) Liposomal clodronate treatment commonly used to deplete monocytes/macrophages showed a minimal effect on ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (IBA1) transcriptional expression in DRGs (Clodronate × Vehicle groups, p = 0.012), but a drastic transcriptional reduction of IBA1 in spleen tissues (Clodronate × Vehicle groups, p = 0.001) of mice 10 days after paclitaxel (n=4–5 male mice/group, t-test, *p<0.05, ***p < 0.001 compared to vehicle).
