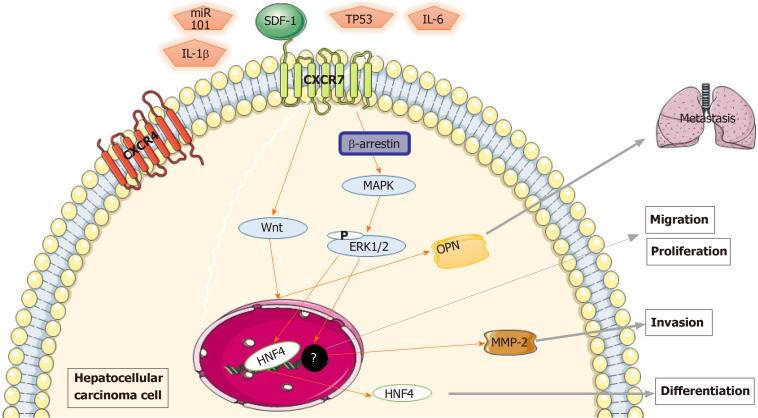
Figure 2.
Mechanism of chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 promoting the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 (CXCR7) contributed to hepatocellular carcinoma growth, including extracellular regulated protein kinases 1/2, and invasiveness via the promotion of matrix metalloproteinase 2 expression; CXCR7- mitogen-activated protein kinases-hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α cascade is the general pathway in the differentiation of hepatocellular carcinomas. Activated transmembrane CXCR7 activates the Wnt signaling pathway through β-arrestin, causing osteopontin expression, which in turn stimulates the ability of tumor cells to metastasize. Several regulators, including tumor protein 53, interleukin-6 and interleukin-1β, are potential upstream regulators of CXCR7-induced signaling. CXCR7: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7; ERK1/2: Extracellular regulated protein kinases 1/2; MMP-2: Matrix metalloproteinase 2; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinases; HNF4α: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α; OPN: Osteopontin; TP53: Tumor protein 53; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β.