Figure 5.
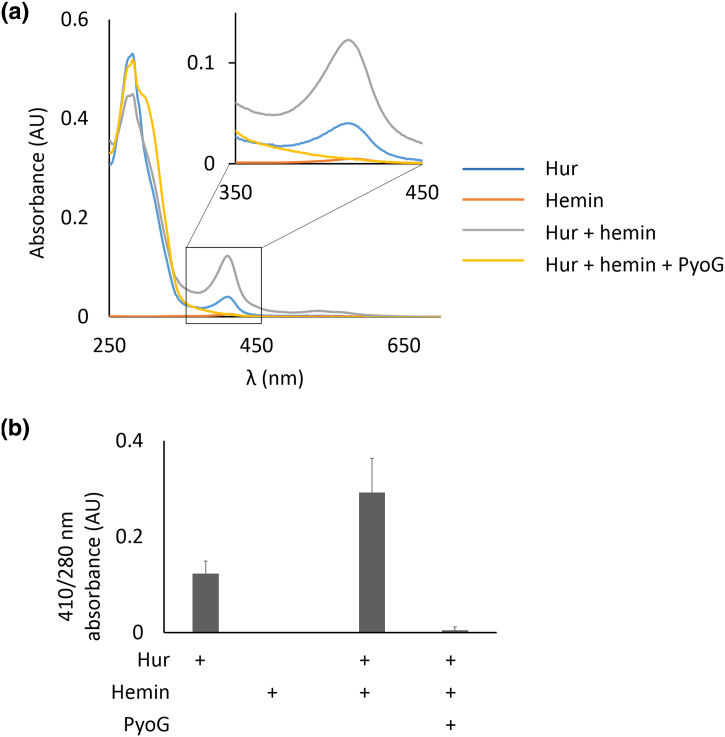
Hur binds hemin, a source of iron for P. aeruginosa in mammalian hosts. Hemin binding to Hur can be blocked by PyoG. (a) Pull-down of hemin with 10 μM His-tagged Hur, in the presence and absence of 10 μM PyoG lacking a purification tag. Proteins were mixed with a 100 × molar excess of hemin and bound to nickel beads. Beads were then washed of unbound protein and hemin. Absorbance spectra of eluate were measured to detect changes in the 410-nm hemin peak (enlarged in the upper corner). Representative absorbance spectra are shown. The 410-nm peak is increased if Hur is exposed to excess hemin, and no hemin peak can be observed if Hur was mixed with PyoG. No considerable 410-nm peak in the protein free control, containing hemin only, confirms that unbound hemin was washed off the beads and makes no contribution to the 410-nm absorbance in the eluate. (b) Ratio between the hemin 410-nm peak and the protein 280-nm peak in the eluate indicates that Hur binds hemin in vitro, which is blocked in the presence of PyoG. Mean of three technical repeats with standard deviations is shown.