Figure 5.
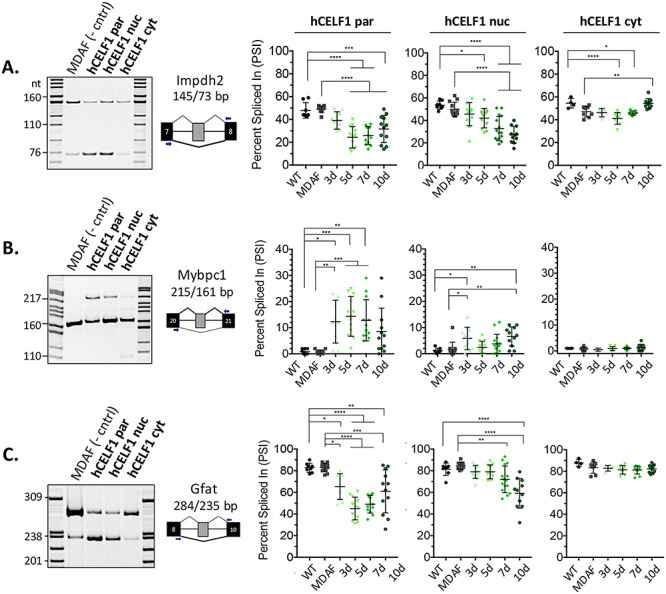
hCELF1par and hCELF1nuc derivatives display functionality in vivo with characteristic alternative splicing misregulation. To test the functionality of each CELF1 derivative in vivo, RNA was isolated from quadriceps of hCELF1par, hCELF1nuc, hCELF1cyt, MDAF and WT mice at each of the time points. RT-PCR was performed using primers complementary to the constitutive exons flanking the alternative exons of interest. Percent exon inclusion was calculated as the intensity of the top band/intensity of both bands x 100, expressed as percent spliced in (PSI). Splicing events of known CELF1 targets that were tested include (A) 72 nt exon Impdh2, (B) 54 nt exon in Mybpc1 and (C) 49 nt exon in Gfat. In the hCELF1par and hCELF1nuc lines, the splicing events tested show a response compared to the splicing pattern observed in MDAF control. Quantification of WT and MDAF controls are a combination of time points as no significant changes were detected in controls on dox for different time points. For each line and time point, n = 4–7 for males and n = 4–7 for females per genotype. Statistical analysis was conducted with one-way ANOVA. Post hoc analysis was performed using Tukey’s HSD correction. *P-value < 0.05, **P-value < 0.01, ***P-value < 0.001, ****P-value < 0.0001.
