Figure 6.
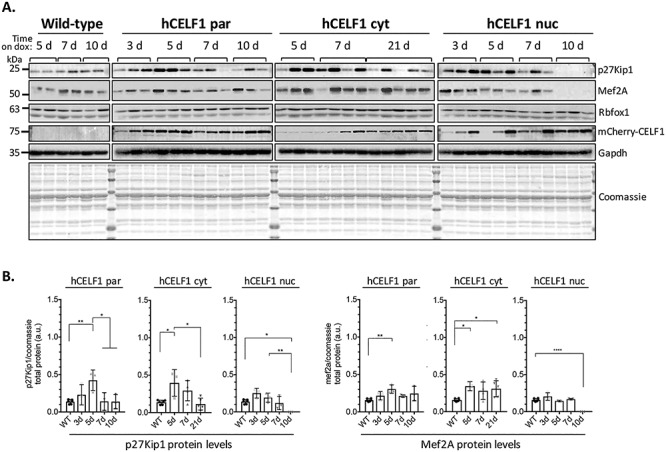
mCherry-CELF1 derivatives display cytoplasmic functionality in vivo with changes in CELF1 translation targets. To test the cytoplasmic functionality of each CELF1 derivative in vivo, protein was isolated from the quadriceps of female hCELF1par, hCELF1nuc, hCELF1cyt and WT (+ dox) animals at each of the time points. (A) Each lane displays protein isolated from different animals. For each protein target tested, all samples were run on one gel and transferred together. In all three lines, the protein levels of CELF1 translation targets p27Kip1 and Mef2A diverge from the levels observed in WT control mice following mCherry-CELF1 expression. (B) Quantification of WT controls are a combination of time points as no significant changes were detected in controls on dox for different time points. Representative Coomassie and Gapdh are shown. Protein signal was measured by densitometry and normalized to total protein as measured by Coomassie. Statistical analysis was conducted with one-way ANOVA. Post hoc analysis was performed using Tukey’s HSD correction. *P-value < 0.05, **P-value < 0.01, ****P-value < 0.0001.
