Figure 1.
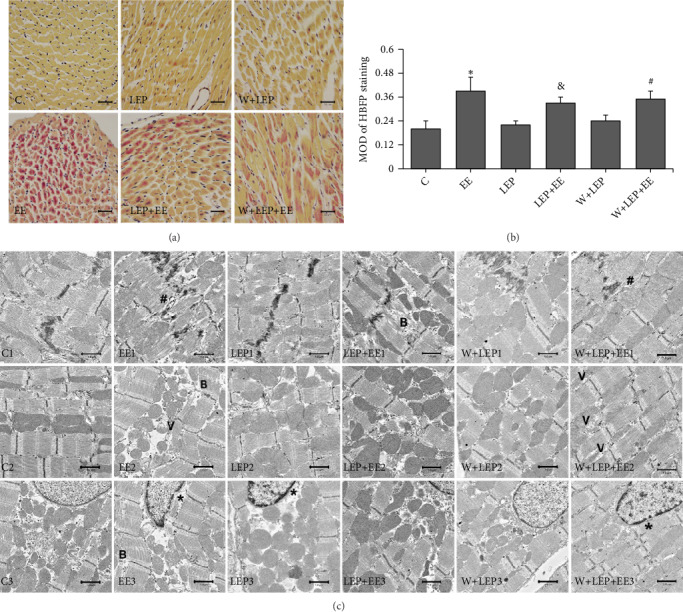
LEP initiated myocardial protection alleviated exhaustive exercise-induced myocardial injury and was partially attenuated by autophagy inhibitor. (a) The changes of myocardial ischemia-hypoxia detected by HBFP staining (×400), bar = 20 μm. Nonischemic myocardial cell showed the light brown color. The ischemic tissue stained a bright crimson red color. The C, LEP, and W+LEP groups displayed a light brown color. Ischemic cardiomyocytes in the EE group stained crimson red. The LEP+EE and W+LEP+EE groups showed red patchy stain. (b) Quantitative analysis of HBFP staining. The EE group compared with the C group, the LEP+EE group compared with the EE group, and the W+LEP+EE group compared with the LEP+EE group were remarkably different. (c) The myocardial ultrastructural changes in six different conditions were observed by TEM (×3,000), bar = 1.0 μm. Exhaustive exercise led to myofibrils breaks (symbol “B”), wide interfibrillar space (symbol “#”), and vacuolate mitochondria (symbol “V”). LEP had normal ultrastructure, but the heterochromatin was slightly marginalized (symbol “∗”). LEP attenuated exhaustive exercise-induced injury in the LEP + EE group. However, wortmannin alleviated the protective effect of LEP. ∗P < 0.05 vs. C, &P < 0.05 vs. EE, #P < 0.05 vs. LEP+EE.
