Figure 2. bNAb characteristics and virus/host factors determine efficacy of passive immunotherapy for HIV-1 prevention and therapy.
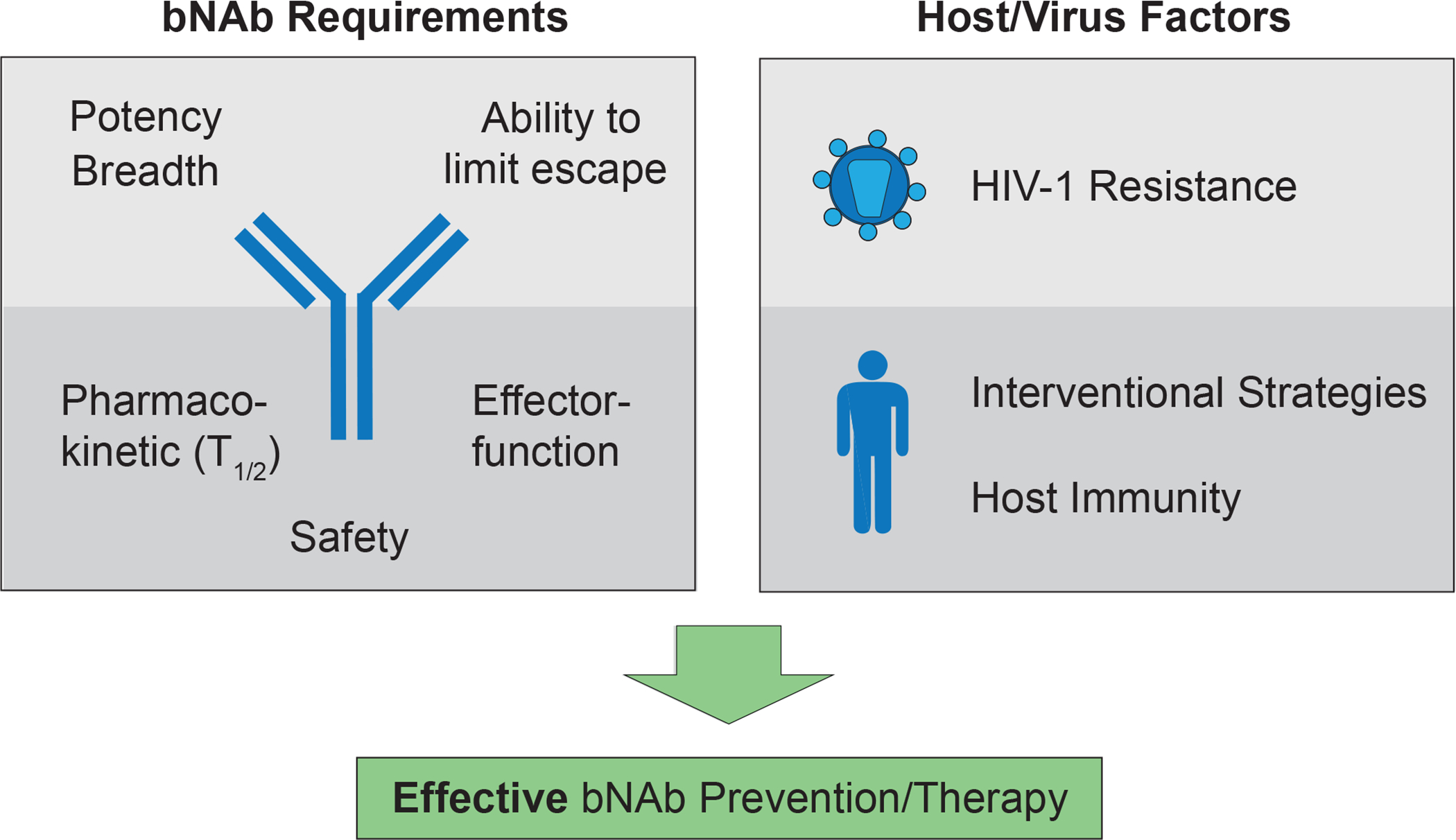
Potency (bNAb concentration required to prevent infection), breadth (neutralization coverage of HIV-1 strains), and the ability to restrict HIV-1 escape pathways are mainly determined by the antigen binding site of the bNAb. In addition, antibody Fc domains interact with host immune cells to mediate antiviral effector functions and can also be modified to increase bNAb half-life. Finally, tolerability and safety are prerequisites for the clinical application of bNAbs. Besides these antibody-intrinsic properties, viral features and host characteristics are critical for efficient bNAb-mediated interventions. Detailed characterization information of the viral quasi-species within an infected individual to identify pre-existing bNAb resistance is relevant for therapy, while the overall prevalence of antibody-sensitivity across circulating viral strains at a population-level is crucial for prevention. The contribution of host immunity and the selection of well-designed strategies will further determine the efficacy of bNAb-mediated interventions.
