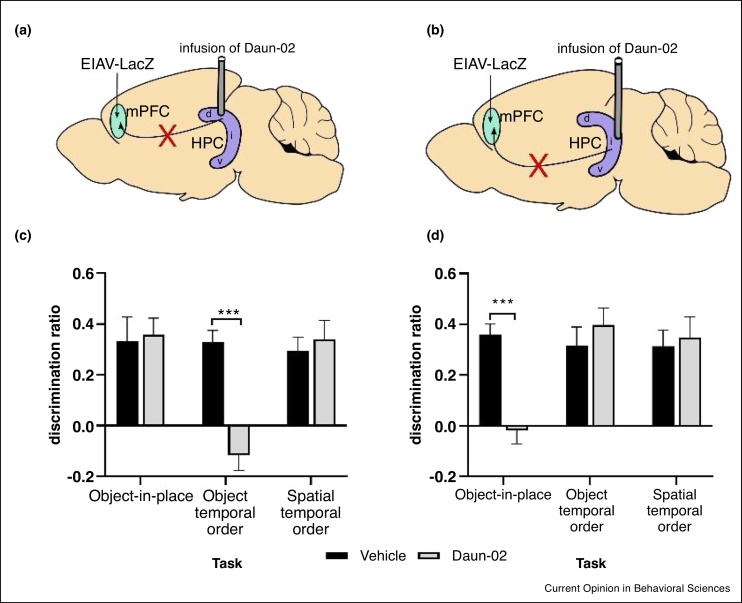
Figure 3.
Deactivation of anatomically distinct projections from CA1 to mPFC reveals contrasting roles in associative recognition memory. (a) and (b) Strategy used to deactivate direct CA1 → mPFC projections. A pseudo-rabies coated lentiviral vector expressing Lac-Z (EIAV-LacZ) injected into medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), and transported retrogradely to the soma of neurons projecting to mPFC. Cannulae were implanted bilaterally either over the dorsal CA1 (dCA1,) or intermediate CA1 (iCA1,). The prodrug Daun-02 is infused through cannula into the HPC where it is converted into daunorubicin resulting in selective deactivation of the CA1 → mPFC. (c) Deactivation of dCA1 → mPFC significantly impairs temporal order memory not object-in-place or temporal location. (d) Deactivation of iCA1 → mPFC significantly impaired object-in-place task but not temporal order or temporal location. Memory performance expressed as mean discrimination ratio (time exploring novel object-time exploring familiar object/total exploration) ±sem. *** p < 0.001. Adapted from Ref. [32].