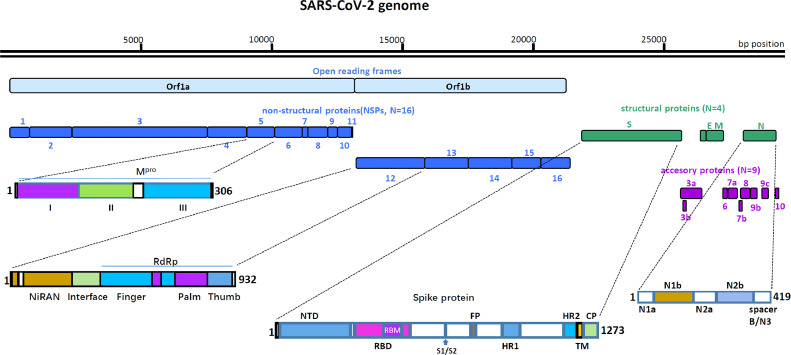
Fig. 1.
Schematic presentation of the SARS-CoV-2 genome organization, and the primary structures of Mpro, NSP12, S protein and N protein. The SARS-CoV-2 genome consists of ∼30 Kb RNA strand. There are 14 ORFs. The first two ORFs at 5′ untranslated regions code for polyprotein (pp1a/ab) that are segmented into 16 NSPs required for virus replication, followed by four structural proteins for spike glycoprotein(S), envelope protein(E), membrane protein(M), and nucleocapsid protein(N). At the 3′ terminus, there are nine accessory proteins (3a, 3b, 6, 7a, 7b, 8, 9b, 9c, and 10). Mpro consists of three domains, Domains I (8–101 aa), II (102–184 aa) and III (201–303 aa). NSP12 has three domains, the RdRp domain (367–920 aa), NiRAN domain (4–28 aa and 69–249 aa) and interface domain (250–365 aa). The RdRp domain consists of three subdomains: the finger subdomain (66–581 and 621–679 aa), the palm subdomain (582–620 and 680–815 aa), and the thumb subdomain (816–920 aa). S glycoprotein is divided into two subunits by protease at the S1/S2 protease cleavage site, Its S1 subunit contains NTD (14–305 aa), RBD (319 –541 aa), and RBM (437–508 aa). Its S2 subunit contains FP (788–806 aa), HR1 (912–984 aa), HR2 (1163–1213 aa), TM (1214–1237 aa) and CP (1238–1273 aa). N protein encompasses two conserved domains, namely the N1b domain (49–175aa), and N2b domain (247–365aa), and three short regions [N1a (1–49aa), N2a (174–247aa), and spacer B/N3 (365–419aa)]. The white box represents loop or non-special structural domain connecting the two domains on either side.