Figure 5. Semiquantitative comparisons of inclusion pathology with various antibodies demonstrate equivalent pathologic αsyn profiles at motor impairment end stage of IM seeded M83+/− mice irrespective of the αsyn C-truncated hPFFs used as inoculum.
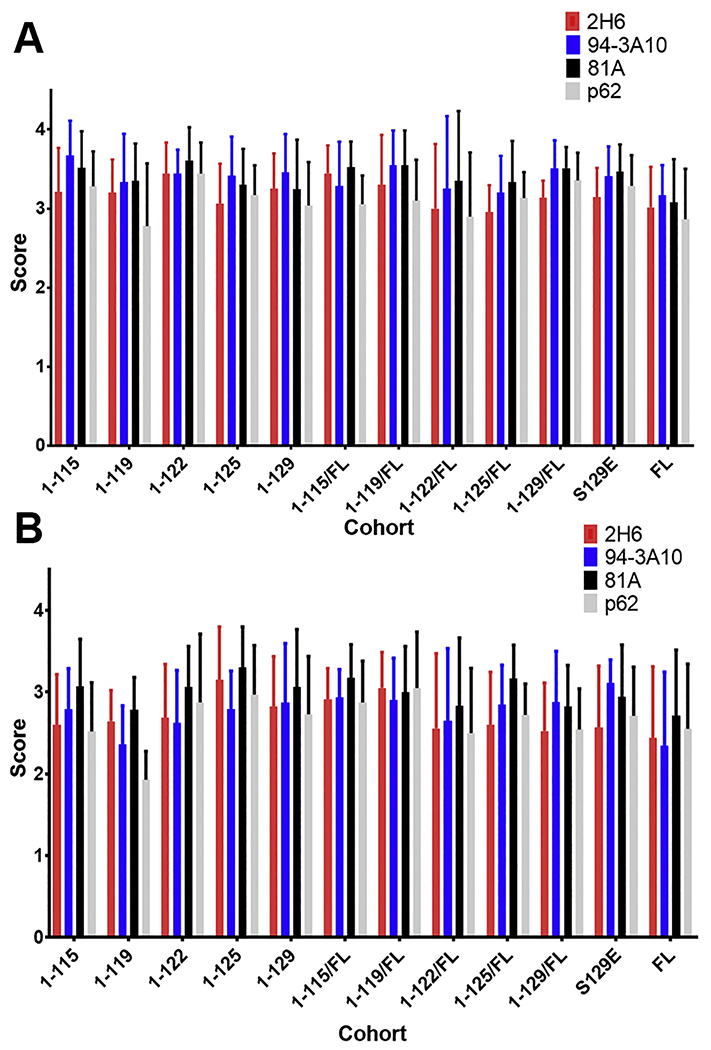
. For cohorts of M83+/− αsyn transgenic mice IM injected with hPFFs of varied compositions (1-115, 1-119, 1-122, 1-125, 1-129, S129E FL, and FL human αsyn or 1:1 mixed fibrils with each C-truncated form of αsyn and FL human αsyn), semiquantitative grading of pathology detected with immunohistochemistry in the (A) spinal cord and (B) pons was performed by 3 independent observers on a 4 point scale for all mice of each cohort using a panel of 4 antibodies with varying epitopes (pSer129 αsyn; 81A, p62-sequestosome-1, 2-21 αsyn; 2H6, 130-140 αsyn; 94-3A10). In general, burden of pathologic αsyn inclusions was increased in the spine relative to the pons for all cohorts of varied PFFs, however no difference was detected between cohorts or between the 4 antibodies within a cohort.
