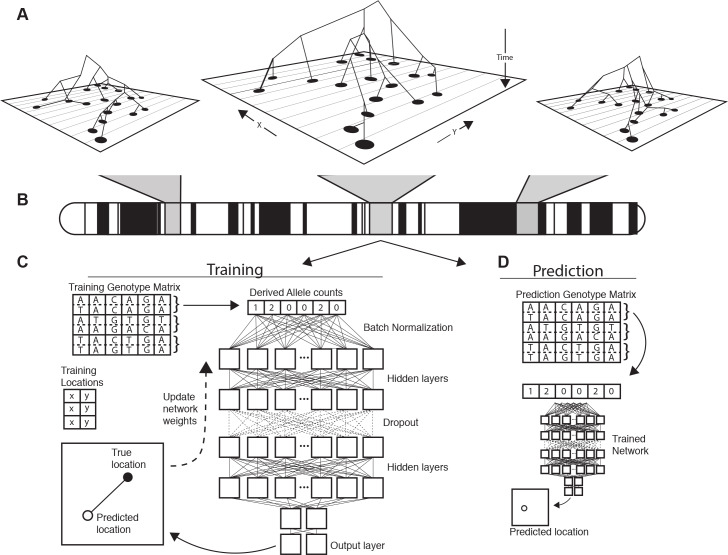
Figure 1. Conceptual schematic of our approach.
Regions of the genome reflect correlated sets of genealogical relationships (A), each of which represents a set of ancestors with varying spatial positions back in time. We extract genotypes from windows across the genome (B), and train a deep neural network to approximate the relationship between genotypes and locations using Euclidean distance as the loss function (C). We can then use the trained network to predict the location of new genotypes held out from the training routine (D).