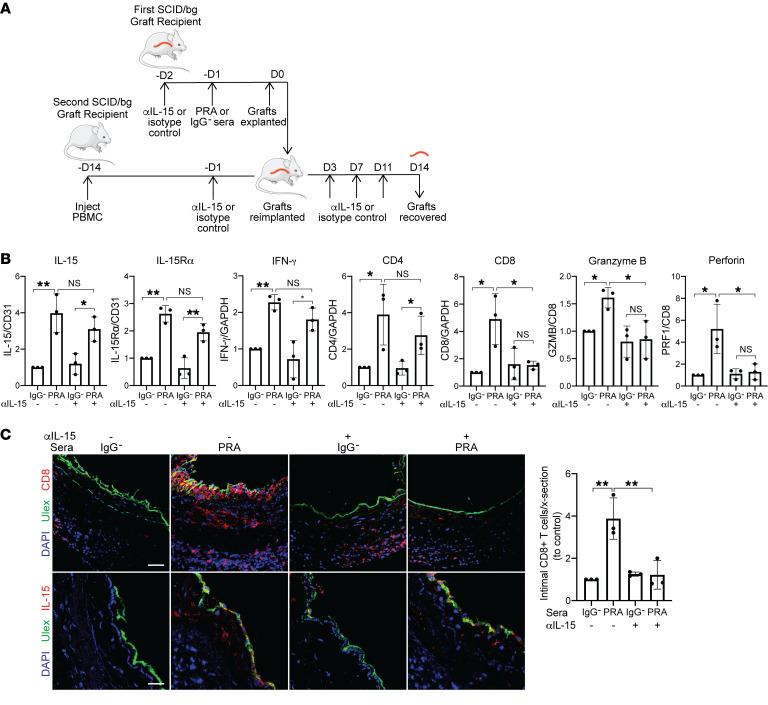
Figure 7. Anti–IL-15 blocking antibody reduces intimal CD8+ T cell infiltration and expression of effector molecules.
(A) Human coronary artery grafts from the same donor were implanted into sets of 4 immunodeficient mice. Recipients were pretreated with anti–human IL-15 blocking antibody (αIL-15) or control isotype antibody before PRA or control sera treatment. Grafts were retransplanted into a second recipient with circulating allogeneic human PBMCs and similarly treated with anti–IL-15 blocking antibody or isotype control (n = 3). (B) qRT-PCR analysis of IL-15 and IL-15Rα (normalized to CD31); IFN-γ, CD4, CD8 (normalized to GAPDH); and granzyme B and perforin (normalized to CD8) in the grafts. Normalized expression is relative to isotype and IgG– control group (n = 3). (C) Immunofluorescence detection of CD8 or IL-15 expression and human endothelium by Ulex in grafts. The intimal infiltrating CD8+ T cells were quantified. Scale bars: 50 μm. Data represent mean SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; 1-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Results shown are representative of 3 artery grafts from 3 different artery donors.