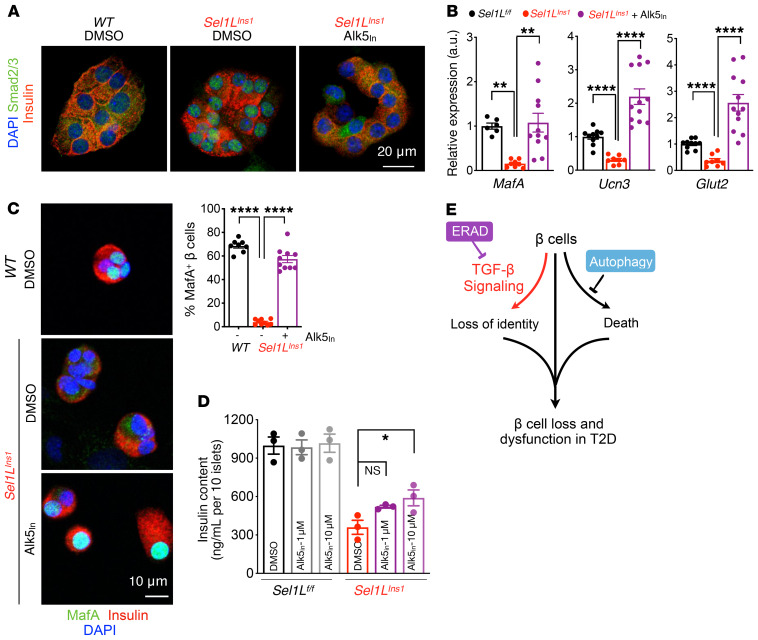
Figure 8. TGF-β signaling links Sel1L to β cell identity.
(A and B) Representative immunofluorescence images of Smad2/3 and insulin (2 independent repeats) (A) and qRT-PCR analysis of β cell gene expression (B) in primary islets treated with vehicle or 10 μM TGF-βRI inhibitor (Alk5in) for 24 hours. qRT-PCR data normalized to WT vehicle controls, from n = 3 biological replicates per genotype. (C) Representative confocal microscopic images of MafA in dispersed primary islets treated with vehicle (DMSO) or TGF-βRI inhibitor Alk5in (2 independent experiments, wider field of view shown in Supplemental Figure 9B). **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001, 1-way ANOVA. (D) Insulin content in primary islets following treatment with either DMSO or indicated dose of TGF-βRI inhibitor for 24 hours (n = 3). *P < 0.05, 2-way ANOVA. (E) Model for distinct effects of ERAD and autophagy in β cell failure in T2D pathogenesis: while autophagy controls cell survival, ERAD maintains β cell identity by suppressing TGF-β signaling. Values are shown as mean ± SEM.