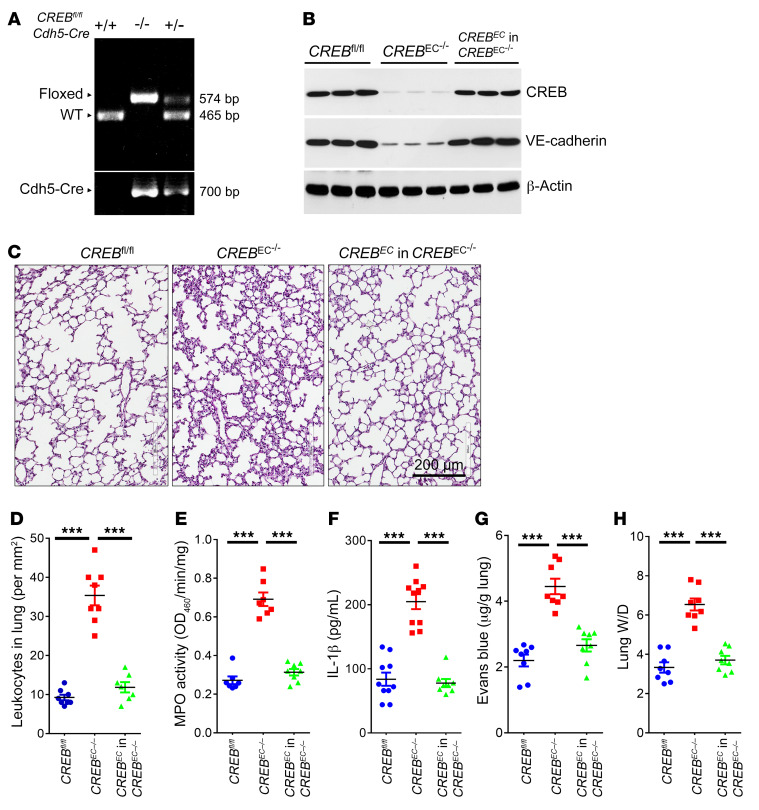
Figure 6. Endothelial CREB expression is required and sufficient for inflammatory lung injury in mice.
(A) EC-specific CREB knockout mice were generated by backcrossing CREBfl/fl mice with Cdh5-Cre-ERT mice. (B) The 2.5-kb VE-cadherin promoter–directed CREB expression constructs were delivered into CREBEC–/– mice (n = 3) by liposome-mediated retroorbital injection for 7 days. Endothelial cells were isolated from mice using anti-CD31 beads. EC-specific CREB restoration was confirmed by Western blot. (C) Representative H&E staining of lung sections from CREBfl/fl, CREBEC–/–, and the EC-CREB–restored CREBEC–/– mice (scale bar: 200 μm; n = 3). (D) Quantitative analysis for leukocyte infiltration in lungs (n = 7). (E) Measurement of lung tissue MPO activity (n = 7). (F) Inflammatory cytokine levels of IL-1β in mice serum were measured by ELISA (n = 7–10). (G) Lung vascular permeability is detected in lungs from CREBfl/fl, CREBEC–/–, and the EC-CREB–restored CREBEC–/– mice (n = 8). (H) The ratio of the wet lung to dry lung weight was determined (n = 8). ***P < 0.001. Statistics obtained from 1-way ANOVA.