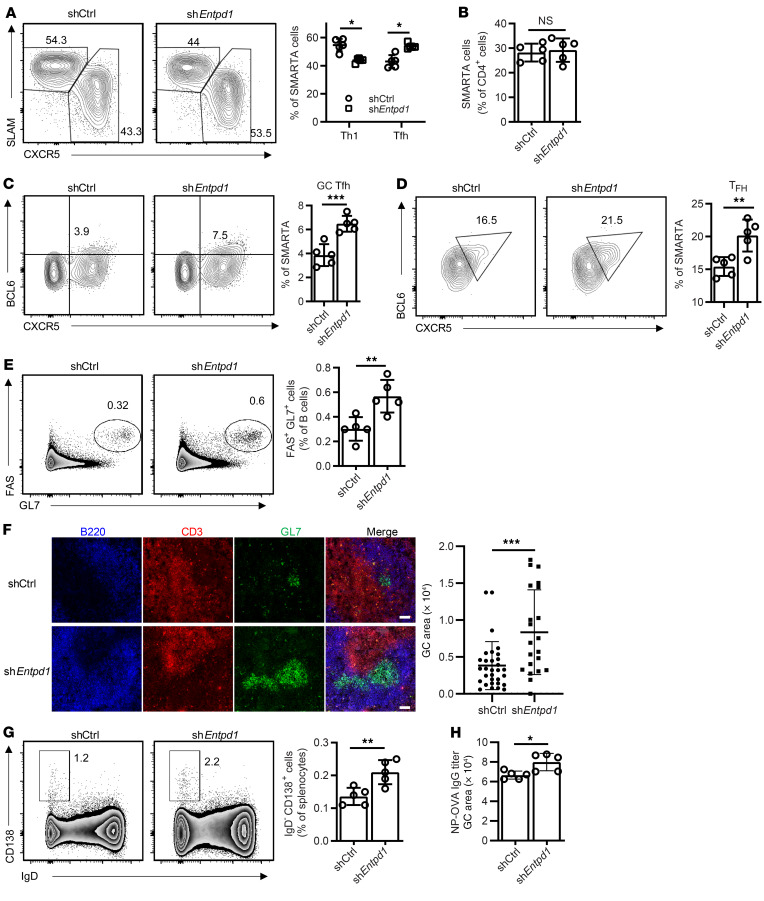
Figure 4. Effect of Entpd1 silencing on murine T cell responses after LCMV infection.
SMARTA CD4+ T cells transduced with the indicated shRNAmir retrovirus were transferred into B6 mice. Spleen cells were analyzed on day 8 (A–C) and day 3 (D) after LCMV infection. (A) Frequencies of Tfh (CXCR5hiSLAMlo) and Th1 (SLAMhiCXCR5lo) SMARTA cells. (B) Frequencies of SMARTA CD4+ T cells as percentage of total CD4+ T cells. (C) Frequencies of GC Tfh (CXCR5+BCL6+) cells. All data are shown as representative contour plots and summary data from 1 of 2 experiments with 4 to 5 mice in each group. (D) CXCR5+BCL6+ Tfh cells were analyzed and quantified by flow cytometry. Data from 1 experiment with 5 mice in each group. (E–H) OT-II CD4+ T cells transduced with the indicated retrovirus were transferred into CD4-knockout mice and analyzed 12 days after immunization with NP-OVA in alum. (E) Frequencies of FAS+GL7+ cells as percentage of total B cells. (F) Histological analysis of spleens from immunized mice. Representative images of B220, CD3, and GL7 staining and comparison of GC areas in mice reconstituted with control and shEntpd1 OT-II T cells. Scale bars: 50 μm. (G) Frequencies of CD138+IgD– plasma cells. Representative contour plots and summary data from 1 experiment with 5 mice in each group. (H) NP-OVA–specific IgG titers. Data shown as mean ± SEM were compared by unpaired 2-tailed t test. *P < 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. NS, not significant.