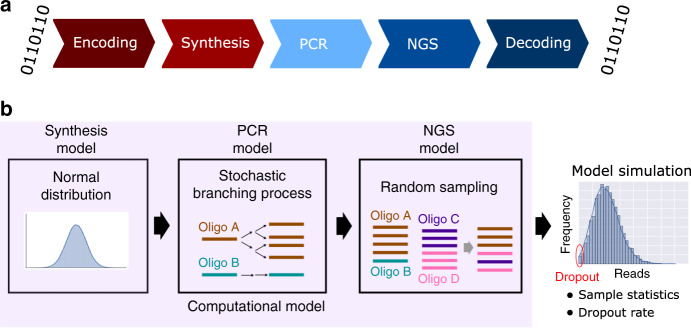
Fig. 1. A DNA storage system model.
a Workflow of DNA data storage. Digital information is first encoded into oligonucleotide (oligo) sequences, resulting in multiple 150-base DNA fragments synthesized using array-based DNA synthesis technology, which are then stored. To read back the stored data, target DNA oligos can be selectively (random-) accessed using polymer chain reaction (PCR), then sequenced via next generation sequencing (NGS), and decoded back to digital information. b The computational model approximates each molecular process in the DNA storage system: it uses a normal distribution for modeling sequence copy numbers from synthesis, a stochastic branching process for PCR, and random sampling for sequencing. The computational model makes predictions for oligo copy distribution to help researchers estimate statistics such as sequence dropout rate.