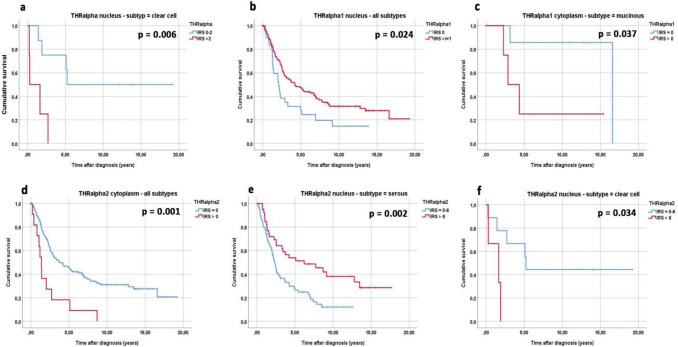
Fig. 2.
Kaplan–Meier estimates of THRα expression, THRα1 expression and THRα2 expression were analyzed. In the clear cell subtype, patients with a high nuclear expression of THRα showed a significantly reduced overall survival compared with patients with a low nuclear expression (a). In addition, high nuclear THRα1 expression was associated with significantly better overall survival in all ovarian cancer subtypes compared to patients with a low nuclear THRα1 expression (b). Patients with high THRα1 expression in the cytoplasm and mucinous subtype had a significantly decreased overall survival compared with those mucinous carcinoma patients with low cytoplasmic expression (c). High cytoplasmic THRα2 expression was associated with a significantly reduced overall survival in all ovarian cancer subtypes compared to patients with a low cytoplasmic THRα2 expression (d). In the serous subtype, patients with a high nuclear expression of THRα2 showed a significantly better overall survival compared with patients with a low nuclear expression (e). Finally, in the clear cell subtype, patients with a high nuclear expression of THRα showed a significantly reduced very low overall survival (all patients deceased within two years) compared to patients with a low nuclear expression (f)